What You Need to Do for Optimal Health with Diabetes
Living with diabetes can be a challenging journey filled with ups and downs. It requires careful management, lifestyle adjustments, and a deep understanding of the condition. This article will explore the various aspects of living with diabetes, providing valuable insights, practical tips, and expert advice to help you effectively manage your health. Whether you have recently been diagnosed or have been living with diabetes for a while, this article supports your path to optimal well-being.
Living with Diabetes: Understanding the Condition
Living with diabetes means navigating a chronic condition that affects how your body regulates blood sugar or glucose. Diabetes occurs when the pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes), or the body doesn’t effectively use its insulin (Type 2 diabetes). Both types require lifelong management and can lead to serious health complications if not properly addressed.
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes, also known as insulin-dependent diabetes, is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This results in a lack of insulin, crucial for moving glucose into the body’s cells for energy. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes require insulin injections or an insulin pump to manage their blood sugar levels.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes, the most common form of diabetes, occurs when the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. This type of diabetes is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, sedentary behavior, and poor dietary choices. Managing Type 2 diabetes typically involves a combination of healthy eating, regular physical activity, oral medications, and, in some cases, insulin therapy.
The Impact of Diabetes on Daily Life
Living with diabetes requires constant vigilance and self-care. The condition affects various aspects of daily life, including diet, exercise, medication management, and emotional well-being. It’s essential to understand the impact diabetes can have on different areas of your life to manage the condition and maintain overall health effectively.
Managing Your Diabetes: Practical Tips and Strategies
Living with diabetes involves making informed choices and implementing strategies that promote stable blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications. Here are some practical tips to help you effectively manage your diabetes and lead a healthy lifestyle:
1. Develop a Balanced Meal Plan
Creating a balanced meal plan is crucial for managing diabetes. Focus on consuming various nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid or limit the intake of sugary beverages, processed foods, and foods high in saturated and trans fats. Additionally, pay attention to portion sizes and the timing of your meals to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
2. Regular Physical Activity: Get Moving!
Engaging in regular physical activity offers numerous benefits for individuals with diabetes. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, manage weight, reduce stress, and boost cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week and strength training exercises. Consult your healthcare team to determine an exercise plan suitable for your needs and abilities.
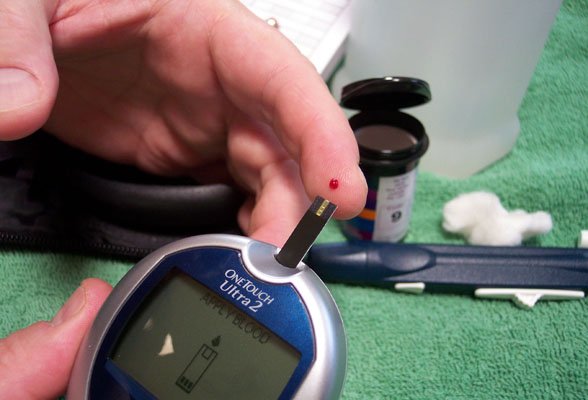
3. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes effectively. Use a blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring system to keep track of your levels throughout the day. This information will help you make informed diet, physical activity, and medication management decisions. Share your records with your healthcare team to identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
4. Medication Management: Stick to Your Plan
If you’re prescribed medication to manage your diabetes, it’s crucial to adhere to your prescribed treatment plan. Take your medication as directed by your healthcare provider and be diligent about maintaining a consistent schedule. Some medications may need to be taken with meals, while others require specific timing. It’s essential to understand the purpose and potential side effects of your medications, as well as any precautions or interactions to be aware of. If you have any concerns or questions about your medication regimen, consult with your healthcare team for guidance.
5. Stay Hydrated and Limit Alcohol Consumption
Proper hydration is important for everyone, but it holds particular significance for individuals living with diabetes. Drinking an adequate amount of water helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels and supports overall well-being. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water per day and adjust your intake based on factors such as activity level, weather conditions, and individual needs.
When it comes to alcohol consumption, moderation is key. Alcohol can interfere with blood sugar control and may cause fluctuations in glucose levels. It’s advisable to limit your alcohol intake and consume alcoholic beverages in moderation, if at all. Remember to monitor your blood sugar levels closely and be aware of how alcohol affects your body.
6. Stress Management: Prioritize Self-Care
Stress can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels and overall health. Managing stress is an important aspect of diabetes care. Find healthy ways to cope with stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in hobbies, connecting with loved ones, or seeking support from a mental health professional. Prioritizing self-care and making time for activities that bring you joy and relaxation can help reduce stress levels and promote overall well-being.
7. Get Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups and screenings are essential for individuals living with diabetes. These appointments allow your healthcare team to monitor your overall health, assess your blood sugar control, and screen for any potential complications. Make sure to schedule routine visits with your primary care physician, endocrinologist, ophthalmologist, and any other specialists recommended by your healthcare team. These proactive measures can help detect and address any health concerns promptly.
8. Educate Yourself and Stay Informed
Knowledge is power when it comes to managing diabetes. Take the initiative to educate yourself about the condition, its management, and the latest advancements in diabetes care. Stay updated on new research, treatment options, and self-care strategies. Reliable sources such as reputable websites, medical journals, and diabetes organizations can provide valuable information. However, consulting with your healthcare team before implementing any changes to your treatment plan or lifestyle is essential.
9. Connect with Support Networks
Living with diabetes can sometimes feel overwhelming, but you don’t have to face it alone. Reach out to support networks and connect with others living with diabetes. Join local support groups, participate in online forums or communities, or consider attending diabetes education classes. Sharing experiences, tips, and emotional support with others who understand your journey can be immensely beneficial and empowering.
10. Embrace Technology
Technology has revolutionized diabetes management, offering various tools and devices to simplify and enhance the process. Consider incorporating technological advancements into your diabetes care routine. Continuous glucose monitoring systems, insulin pumps, smartphone apps for tracking blood sugar levels and medications, and digital platforms for connecting with healthcare providers are just a few examples of how technology can support your diabetes management efforts.
11. Take Care of Your Feet
Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing foot problems due to poor circulation and nerve damage. To protect your feet, practice good foot hygiene, inspect them regularly for any cuts, sores, or signs of infection, and wear comfortable shoes that provide proper support and fit well.
12. Prioritize Dental Care
Oral health is closely linked to overall health; individuals with diabetes are more prone to gum disease and other dental issues. Make sure to maintain good oral hygiene by brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing regularly, and scheduling regular dental check-ups. Inform your dentist about your diabetes diagnosis and work together to develop a comprehensive dental care plan that suits your needs.
13. Traveling with Diabetes
Traveling can pose unique challenges for individuals with diabetes, but proper planning and preparation can be an enjoyable experience. When traveling, ensure you have ample medication and supplies to last the duration of your trip, including extra in case of unforeseen circumstances. Carry a medical ID bracelet or card that identifies you as a person with diabetes, and familiarize yourself with the healthcare resources available at your destination. Consult your healthcare provider before traveling to discuss any specific precautions or adjustments to your treatment plan.
14. Handling Sick Days
Illness or infection can affect blood sugar levels and require special attention when you have diabetes. It’s important to have a sick day plan in place. Make sure to stay hydrated, continue taking your medication or insulin as directed, and monitor your blood sugar levels more frequently. Reach out to your healthcare team for guidance on adjusting your medication doses, if necessary. If your illness persists or worsens, seek medical attention promptly.
15. Pregnancy and Diabetes
Managing diabetes during pregnancy requires careful planning and monitoring. If you have diabetes and are planning to conceive or are already pregnant, working closely with your healthcare team to ensure optimal blood sugar control is essential. Regular prenatal care, proper nutrition, regular exercise, and close monitoring of blood sugar levels are crucial for a healthy pregnancy and to reduce the risk of complications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some common questions about living with diabetes, with simple and concise answers:
Q1: Can diabetes be reversed? A1: While Type 2 diabetes can sometimes be managed or even reversed through lifestyle changes such as weight loss, healthy eating, and increased physical activity, Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition that cannot be reversed.
Q2: What are the long-term complications of diabetes? A2: Long-term complications of diabetes can include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, eye problems, and foot problems. However, the risk of complications can be reduced with proper management and control of blood sugar levels.
Q3: Can I still enjoy my favorite foods with diabetes? A3: Yes, you can still enjoy a wide variety of foods with diabetes. The key is moderation, portion control, and making healthier choices. Working with a registered dietitian can help you create a balanced meal plan incorporating your favorite foods while managing your blood sugar levels.
Q4: Is it safe to exercise with diabetes? A4: Yes, exercise is generally safe and beneficial for individuals with diabetes. However, it’s important to consult your healthcare team before starting or changing your exercise routine, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Q5: Can stress affect my blood sugar levels? A5: Yes, stress can affect blood sugar levels. When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones that can cause your blood sugar to rise. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, relaxation techniques, or seeking support, is important for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Q6: Can I drink alcohol if I have diabetes? A6: Moderate alcohol consumption may be acceptable for some individuals with diabetes. However, alcohol can affect blood sugar control, so monitoring your levels and drinking in moderation is crucial. It’s advisable to consult with your healthcare team to determine
Q6: Can I drink alcohol if I have diabetes? A6: Moderate alcohol consumption may be acceptable for some individuals with diabetes. However, alcohol can affect blood sugar control, so monitoring your levels and drinking in moderation is crucial. It’s advisable to consult with your healthcare team to determine if alcohol is safe for you and to understand any potential interactions with your medications.
Living with diabetes requires commitment, education, and ongoing support. By implementing healthy lifestyle choices, closely monitoring blood sugar levels, adhering to medication regimens, and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their condition and lead fulfilling lives. Remember, you are not alone on this journey. Connect with support networks, stay informed, and prioritize self-care to navigate the challenges and embrace the possibilities of living with diabetes.
Incorporating these strategies into your daily routine can help you maintain stable blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve your overall quality of life. Remember, managing diabetes is a lifelong journey, and adapting and adjusting along the way is essential. Stay proactive, ask questions, and seek your support to thrive with diabetes.
Could You Be At Risk? New Reports Terrifying Estimates Regarding the Global Diabetes Epidemic.
Diabetes has emerged as a significant global health concern, with its prevalence skyrocketing over the past few decades. The impact of this chronic metabolic disorder extends beyond individuals, affecting families, communities, and healthcare systems worldwide. In this article, we delve into the alarming projections of diabetes rates and their implications for the future. By exploring the factors contributing to this epidemic, understanding the different types of diabetes, and emphasizing the importance of prevention and management, we aim to shed light on this pressing issue.
The Alarming Projections
A recent report in the Daily Mail highlights the projected rise in diabetes rates, indicating a staggering increase from 529 million cases in 2021 to an estimated 1.3 billion cases by 2050. These numbers paint a grim picture of the future, urging us to take immediate action to mitigate the impact of this epidemic. The implications are far-reaching, encompassing both individual health outcomes and the strain placed on healthcare systems worldwide.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels resulting from either insufficient insulin production or ineffective utilization of insulin. There are primarily three types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: This form of diabetes typically develops in childhood or adolescence. It occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections for life to regulate their blood sugar levels.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is the most common form, accounting for most diabetes cases globally. It usually develops in adulthood, although it increasingly affects younger individuals due to rising obesity rates and sedentary lifestyles. In type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough insulin to meet the body’s needs. Lifestyle modifications like healthy eating, regular exercise, and medication are vital to managing type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational Diabetes: Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes cause insulin resistance. While it usually resolves after childbirth, women with gestational diabetes are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Factors Contributing to the Diabetes Epidemic
Multiple factors contribute to the rising prevalence of diabetes globally. These include:
- Obesity: The increasing prevalence of obesity plays a significant role in the diabetes epidemic. Excess body weight and sedentary lifestyles contribute to insulin resistance and the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Unhealthy Diets: Diets high in processed foods, sugary beverages, and unhealthy fats contribute to weight gain and the risk of developing diabetes. A lack of nutritious food exacerbates this issue, particularly in underserved communities.
- Sedentary Lifestyles: Modern lifestyles characterized by long hours of sitting, limited physical activity, and a decline in exercise contribute to the risk of developing diabetes. Regular physical activity is crucial in preventing and managing diabetes.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing diabetes. While genetic factors alone do not cause diabetes, they can increase susceptibility when combined with environmental and lifestyle factors.
Prevention and Management Strategies
To combat the diabetes epidemic, a comprehensive approach focusing on prevention, early detection, and effective management is crucial. Here are some key strategies:
- Public Health Campaigns: Increasing awareness about diabetes risk factors, promoting healthy lifestyles, and encouraging regular screenings can significantly impact prevention and early detection.
- Healthy Eating: Emphasizing the importance of balanced, nutrient-dense diets can help prevent obesity and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Encouraging the consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean, and healthy fats while limiting processed foods and sugary beverages can contribute to diabetes prevention.
- Regular Physical Activity: Encouraging individuals to exercise regularly is crucial for diabetes prevention and management. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, promotes weight management, and enhances cardiovascular health. Aim for aerobic workouts, strength training, and flexibility exercises. You can discover the benefits of regular physical activity (afternoon and walking) for diabetes control.
- Routine Screening and Early Detection: Regular health check-ups should include screenings for diabetes risk factors, such as blood sugar levels and body mass index (BMI). Early detection allows for timely intervention and management of the condition.
- Medication and Insulin Therapy: For individuals with diabetes, appropriate medication and insulin therapy may be necessary to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. This should be done under the guidance and supervision of healthcare professionals.
- Diabetes Education and Support: Providing access to diabetes education and support programs is crucial for individuals with diabetes. These programs can offer valuable information, guidance on lifestyle modifications, and emotional support to help individuals effectively manage their condition.
- Collaboration Between Healthcare Professionals: Establishing a collaborative approach among healthcare professionals, including primary care physicians, endocrinologists, dietitians, and diabetes educators, ensures comprehensive care for individuals with diabetes. The care plan should include regular follow-ups, medication adjustments, and lifestyle counseling.
The projected rise in global diabetes rates is a cause for concern, necessitating urgent action to curb this epidemic. By understanding the different types of diabetes, addressing the factors contributing to its prevalence, and implementing effective prevention and management strategies, we can strive to mitigate the impact of this chronic condition. Through public health initiatives, education, healthy lifestyle promotion, and accessible healthcare services, we can work towards a healthier future where diabetes rates are reduced and individuals with diabetes can lead fulfilling lives. Let us join forces in combating the diabetes epidemic and prioritizing the health and well-being of our communities.

Drinking Tea and Diabetes Management: Is There Benefits?
Welcome to Diabetes Life Balance! This article will explore the potential benefits of tea and diabetes management. Tea, mainly green tea, has gained attention for its positive effects on blood sugar regulation and overall health. Join us as we delve into tea and discover its impact on diabetes management.
Discover the Power of Tea
Tea has long been celebrated for its refreshing taste, but its benefits go beyond mere enjoyment. Emerging research suggests that tea when incorporated into a comprehensive diabetes management plan, can provide valuable support. Join us as we uncover the potential benefits of different tea varieties and their role in managing diabetes effectively.
The Potential of Green Tea in Diabetes Management
Unlocking the Wonders of Green Tea
Green tea, derived from the Camellia sinensis plant, has captured attention for its exceptional health properties. Let’s delve into the potential benefits of green tea in diabetes management and how it can positively influence blood sugar levels.
Supporting Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Regulation
Green tea’s bioactive compounds, including polyphenols and antioxidants, have shown promise in improving insulin sensitivity. Green tea may help regulate blood sugar levels effectively by enhancing the body’s response to insulin. Incorporating green tea into your routine, a balanced diet and regular exercise can improve glucose control.
Harnessing the Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation is often associated with diabetes and its complications. Green tea’s abundance of antioxidants offers anti-inflammatory properties that may mitigate the impact of inflammation on diabetes management. By reducing inflammation, green tea can support overall well-being and potentially reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Mechanisms Behind Green Tea’s Benefits
Green tea’s positive effects on diabetes management can be attributed to several mechanisms:
Improved Insulin Sensitivity: The polyphenols in green tea may enhance the body’s sensitivity to insulin, facilitating better glucose utilization.
Inhibition of Alpha-Amylase: Green tea’s polyphenols have the potential to inhibit alpha-amylase, an enzyme responsible for carbohydrate digestion. This inhibition can help regulate postprandial blood sugar spikes.
Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Properties: The antioxidants in green tea combat oxidative stress and reduce chronic inflammation, which can contribute to improved diabetes management.
Exploring Other Tea Varieties and Their Impact
While green tea takes the spotlight, other tea varieties have their potential benefits for diabetes management:
Black Tea: Unveiling its Powers
Black tea, known for its rich flavor, contains flavonoids that may reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Regular consumption of black tea has been associated with improved glucose metabolism and decreased insulin resistance. Adding a cup of black tea to your daily routine can be a flavorful and beneficial choice for managing diabetes.
Herbal Tea: Nurturing Well-being
Herbal teas, such as chamomile and hibiscus, offer unique properties that can positively impact diabetes management. Chamomile tea, for instance, has been linked to improved glycemic control and decreased complications associated with diabetes. Including herbal teas in your diabetes management plan can introduce a nice variety while potentially benefiting your overall well-being.
Incorporating Tea into Your Diabetes Management Routine
Safely Embracing Tea’s Potential
As you incorporate tea into your diabetes management routine, it’s essential to keep the following considerations in mind:
Caffeine Content: Tea contains varying levels of caffeine. While generally lower than coffee, being mindful of your caffeine intake is essential. Excessive caffeine consumption can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure. Opting for decaffeinated tea versions or limiting consumption to moderate levels can help mitigate potential side effects.
Avoid Sweetened Varieties: Flavored and sweetened teas may contain added sugars or artificial sweeteners, adversely affecting blood sugar levels. Choose natural, unsweetened tea options to maximize the potential benefits without compromising your diabetes management goals.
Individual Variations: Each person’s response to tea consumption may vary. Monitoring your blood sugar levels and working closely with your healthcare provider can help determine the optimal amount and frequency of tea consumption that aligns with your specific needs.
Incorporating tea into your diabetes management routine should be seen as a complementary approach rather than a standalone solution. Tea alone cannot replace prescribed medication, a balanced diet, or regular exercise. It is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider to ensure that tea consumption aligns with your overall diabetes management plan.
Enhancing Your Knowledge of Diabetes Management
At Diabetes Life Balance, we are committed to providing comprehensive and accurate information to support your journey toward managing diabetes effectively. We invite you to explore the following resources for further insights:
Discover the connection between diet and diabetes management.
Uncover the benefits of regular physical activity (afternoon and walking) for diabetes control.
Learn about the latest advancements in diabetes research and treatment.
By exploring these resources, you can expand your knowledge base and continue making informed decisions to live a balanced and healthy life with diabetes.
Tea, mainly green tea, holds promise as a complementary approach to diabetes management. With its potential to improve insulin sensitivity, regulate blood sugar levels, and combat inflammation, tea can be valuable in supporting overall well-being. Incorporating tea into your routine should be done in consultation with your healthcare provider, considering individual variations and other aspects of your diabetes management plan.
Remember, tea is not a magical cure for diabetes. It works best when combined with prescribed medication, a balanced diet, regular exercise, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. By adopting a comprehensive approach to diabetes management and utilizing the potential benefits of tea, you can take positive steps toward achieving optimal health and well-being.

Explaining the Surge of Diabetes Diagnosis During the Pandemic?
In the turmoil of the COVID-19 pandemic, a parallel health crisis loomed – an unprecedented surge in diabetes cases worldwide. The intertwining of these two healthcare calamities warrants a comprehensive examination. This article presents a complex analysis of the reasons behind the escalation in diabetes cases during the COVID-19 pandemic and strategies to counteract this rising tide.
The Convergence of Two Health Crises
The Vicious Cycle of Diabetes and COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic wreaked havoc globally. During this period, there was a significant rise in diabetes cases. The relation between COVID-19 and diabetes is reciprocal – while diabetes predisposes individuals to severe COVID-19 infections, the virus can also trigger the onset of diabetes.
The Role of Inflammatory Responses
COVID-19 infections often cause excessive inflammatory responses. In some individuals, this leads to autoimmune reactions wherein the body’s immune system targets the pancreatic beta cells, which are crucial for insulin production, leading to diabetes.
Psychological Factors at Play
Pandemic-Induced Stress and Diabetes
The anxiety and stress associated with the pandemic have profoundly impacted blood sugar levels. The stress hormones cortisol and adrenaline lead to elevated blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of diabetes.
The Emotional Eating Phenomenon
For many, food became a refuge from the emotional turmoil. Emotional eating, especially of high-calorie comfort foods, contributed to weight gain and the onset of type 2 diabetes.
Lifestyle Alterations and Their Impact
Sedentary Lifestyles and Physical Inactivity
The lockdowns and restrictions led to more sedentary lifestyles. The lack of physical activity is a significant factor in developing type 2 diabetes. If you need more information on the best way to exercise to help prevent Diabetes, read this post, or you can look at this.
Changes in Dietary Patterns
People resorted to consuming more processed and fast foods, often high in sugar and unhealthy fats, contributing to obesity and insulin resistance.
Economic Constraints and Health Choices
Financial Strains Affecting Dietary Choices
The pandemic caused economic hardships, leading many to opt for cheaper, calorie-dense foods lacking in nutritional value, fueling the diabetes epidemic.
Reduced Access to Healthcare
Economic constraints also meant that many could not afford regular health checks, allowing prediabetes to progress unchecked into full-blown diabetes.
Strategies to Counteract the Diabetes Surge
Promoting Physical Activity
Encouraging regular physical activity, even within the confines of one’s home, can play a vital role in controlling blood sugar levels.
Emphasizing Nutritional Education
Educational campaigns focusing on the importance of a balanced diet can help make informed dietary choices.
Mental Health Support
Providing accessible mental health support can alleviate pandemic-related stress and reduce emotional eating.
Strengthening Healthcare Systems
Improving access to healthcare, especially for the economically disadvantaged, is crucial in the early detection and management of diabetes.
The surge in diabetes cases during the COVID-19 pandemic is a consequence of a complex interplay between medical, psychological, lifestyle, and economic factors. Address of medical, psychological, lifestyle, and economic factors. Addressing this requires a multifaceted approach encompassing lifestyle modifications, mental health support, nutritional education, and bolstering healthcare systems. Collectively, we can stem the tide and safeguard our communities against the double onslaught of COVID-19 and diabetes.
References
- Rubino, F., Amiel, S. A., Zimmet, P., Alberti, G., Bornstein, S., Eckel, R. H., … & Herman, W. H. (2020). New-onset diabetes in Covid-19. New England Journal of Medicine, 383(8), 789-790.
- American Diabetes Association. (2021). Stress. Retrieved from https://www.diabetes.org/diabetes/mental-health/stress
- Sidor, A., & Rzymski, P. (2020). Dietary Choices and Habits during COVID-19 Lockdown: Experience from Poland. Nutrients, 12(6), 1657.
- Pareek, M., Bangash, M. N., Pareek, N., Pan, D., Sze, S., Minhas, J. S., … & Khunti, K. (2020). Ethnicity and COVID-19: an urgent public health research priority. The Lancet, 395(10234), 1421-1422.
- World Health Organization. (2021). Physical Activity. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/physical-activity

The NEW “Secret”: Early-Day Fasting Reduces Your Risk of Diabetes
Embarking on the journey to a healthier life is monumental. Early-Day Fasting is an astonishingly potent tool among the myriad health strategies. In this article, we unveil how this remarkable dietary approach can significantly lower your risk of diabetes.
The Dawn of New Beginnings: Understanding Early-Day Fasting
Early-Day Fasting is a system that combines intermittent fasting with meal timing. It emphasizes consuming most of our daily calories early and fasting (not eating) throughout the rest of the day.
What Constitutes Early-Day Fasting?
- Morning Feast: A substantial portion of daily caloric intake happens in the morning.
- Limited Evening Consumption: A drastic reduction or complete abstaining from food post-afternoon.
- Fasting Window: A fasting period, typically lasting 14-18 hours until the following day.
Scientific Revelations: Early-Day Fasting’s Role in Combating Diabetes
Extensive research has shown that Early-Day Fasting could be our secret weapon in the fight against diabetes. But what exactly do the studies and reporters tell us? Lets now delve into the science.
Chronobiology – The Rhythmic Symphony of Our Bodies
Our bodies harbor an internal clock, termed the circadian rhythm. And this ‘clock’ influences our metabolism. As the sun goes down, so does our metabolic efficiency. Early-Day Fasting capitalizes on the body’s peak metabolic periods.
Insulin Sensitivity – The Guardian Against Glucose
Early-Day Fasting boosts insulin sensitivity. Enhanced sensitivity facilitates glucose uptake into cells, keeping blood sugar levels in check. When we have too much sugar (glucose), our bodies create insulin to help us absorb it into cells. As with anything, prolonged exposure leads to desensitization. That means if our body constantly releases insulin, our sensitivity lowers. Leading to the insulin provided losing its efficacy.
Reduced Oxidative Stress – The Shield Against Cellular Damage
Lower evening caloric intake minimizes the production of free radicals. This mitigates oxidative stress, which is instrumental in preventing diabetes.
A Tapestry of Success: Real-Life Results
Phenomenal Early Time-Restricted Feeding (eTRF) Study
Several studies vividly show Early-Day Fasting’s triumphs in diabetes reduction. One such study on the impact of afternoon and evening fasting was referred to as the eTRF study. This study and subsequent report promote eating the last meal by mid-afternoon and fasting until breakfast. Participants manifested improved insulin sensitivity, β-cell function, blood pressure, oxidative stress levels, and appetite.
8-Hour Diet Study Revelations
Participants consumed food within an 8-hour window, focusing on morning and early afternoon meals. They showed remarkable reductions in insulin resistance and inflammatory markers.
Incorporating Early-Day Fasting: Your Game Plan
Successful adoption of Early-Day Fasting entails meticulous planning. You will need to appreciate that changing your diet can and is challenging. You will feel hungry when you start fasting. But don’t give up. The benefits will outweigh the short, uncomfortable time we deal with as our bodies adjust to our new eating schedule.
The Morning Powerhouse
Construct a nutritionally-dense breakfast. Include whole grains, proteins, healthy fats, and fruits. The only sugars you should incorporate in your morning meal are those found naturally in fruits. Avoid processed or refined sugars as much as possible.
Mid-Day Nutritional Prowess
Create a balanced lunch that will satisfy you without feeling hungry. Meals that lead to feeling full include vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. We must make it as easy as possible to change our eating habits successfully. And eating meals that do not leave us wanting more is imperative if we make this lifestyle change permanent.
Traversing the Evening with Caution
As the sun sets, limit food consumption. Opt for light, easily digestible fare – if you must have this meal. You will not starve by skipping this evening meal. The longer you can go without eating, the more time your body has to accept the glucose already in your blood. This time will allow the insulin to do its job and gradually regain effectiveness.
Early-Day Fasting as a Cornerstone for Health
With its scientific underpinning and real-life success stories, Early-Day Fasting emerges as a compelling strategy to reduce the risk of diabetes. Embrace this dietary symphony and unlock the doors to a healthier future.
Further reading
- Sutton, E. F., Beyl, R., Early, K. S., Cefalu, W. T., Ravussin, E., & Peterson, C. M. (2018). Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Insulin Sensitivity, Blood Pressure, and Oxidative Stress Even without Weight Loss in Men with Prediabetes. Cell Metabolism, 27(6), 1212-1221. Link to the article
- Moro, T., Tinsley, G., Bianco, A., Marcolin, G., Pacelli, Q. F., Battaglia, G., … & Paoli, A. (2016). Effects of eight weeks of time-restricted feeding (16/8) on basal metabolism, maximal strength, body composition, inflammation, and cardiovascular risk factors in resistance-trained males. Journal of Translational Medicine, 14(1), 290. Link to the article
- Hatori, M., Vollmers, C., Zarrinpar, A., DiTacchio, L., Bushong, E. A., Gill, S., … & Panda, S. (2012). Time-restricted feeding without reducing caloric intake prevents metabolic diseases in mice fed a high-fat diet. Cell Metabolism, 15(6), 848-860. Link to the article
- Gabel, K., Hoddy, K. K., Haggerty, N., Song, J., Kroeger, C. M., Trepanowski, J. F., … & Varady, K. A. (2018). Effects of 8-hour time restricted feeding on body weight and metabolic disease risk factors in obese adults: A pilot study. Nutrition and Healthy Aging, 4(4), 345-353. Link to the article
These references provide scientific insights into the impact of Early-Day Fasting on diabetes risk reduction.

Exercise in the Afternoon for Improved Type 2 Diabetes Management
Discover the transformative potential of integrating exercise into your daily routine, with a focus on the afternoon hours, in effectively managing Type 2 Diabetes. In this article, we provide an insightful exploration into the world of fitness backed by emerging scientific evidence.
The Ongoing Battle Against Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes is a burgeoning global health concern. This metabolic disorder compromises your body’s ability to regulate blood sugar. Tackling it head-on requires an informed, multifaceted approach.
The Cornerstone: Exercise and Its Significance
Rejuvenating Your Body’s Dynamics
Exercise is a cornerstone in the management of Type 2 Diabetes. Engaging your muscles through physical activity enhances insulin sensitivity and aids in stabilizing blood glucose levels. This combination is essential in keeping Type 2 Diabetes in check.
Optimal Timing: The Afternoon Advantage
Aligning with Your Body’s Clock
Our bodies are governed by internal clocks known as circadian rhythms, which dictate various physiological processes. Engaging in physical activity during the afternoon appears to align seamlessly with these rhythms, yielding amplified benefits.
The Afternoon Surge in Insulin Sensitivity
Exercising in the afternoon has been associated with a surge in insulin sensitivity compared to morning workouts. Enhanced insulin sensitivity is invaluable as it allows your cells to utilize glucose more efficiently, keeping blood sugar levels balanced.
Crafting a Sustainable Afternoon Exercise Routine
Diverse Workouts for Holistic Benefits
A well-rounded exercise routine incorporating cardiovascular activities such as brisk walking or swimming, alongside resistance training, is advisable. These exercises impact blood glucose levels and contribute to overall physical and mental well-being.
Consistency is Key
Developing a sustainable exercise routine is vital. Dedicate time daily for physical activity, or at least most days of the week.
Stay Informed and Adapt
It’s imperative to regularly monitor your blood sugar levels and consult your healthcare provider to make necessary adjustments to your exercise regimen. This ensures a tailored approach that caters to your body’s specific needs.
Being Cautious: Safety Measures
Consult your healthcare professional before initiating any new exercise regimen. It’s prudent to take necessary precautions to avoid complications, especially if you’re dealing with a chronic condition like Type 2 Diabetes.
Embrace the Afternoon: A Catalyst for Change
Incorporating afternoon exercise into your daily routine can be a catalyst for positive change in managing Type 2 Diabetes. Empowered with this knowledge, let’s seize the afternoon, elevating our health and lives.
Your Roadmap to Success
As you embark on this transformative journey, remember that knowledge, consistency, and a positive mindset are your most potent allies. The dedicated afternoon exercise and your unwavering commitment can foster a fulfilling and instrumental lifestyle in combating Type 2 Diabetes.
Engaging with Professionals for Tailored Guidance
Engaging with healthcare professionals is highly beneficial for a personalized approach. They can provide insights and recommendations tailored to your unique needs. Furthermore, diabeteslifebalance.com offers a plethora of resources to support your journey.
Fostering a Community of Like-minded Individuals
Sharing experiences and exchanging information with others taking steps to manage Type 2 Diabetes can be immensely rewarding. Being part of a community can offer the encouragement and motivation necessary to remain steadfast in your goals.
Empowerment Through Education
Staying informed about the latest developments in Type 2 Diabetes management is crucial. With reliable information at your fingertips, you can make more informed decisions that positively impact your health.
The Takeaway: Seizing the Afternoon for A Brighter Tomorrow
Type 2 Diabetes need not be an insurmountable challenge. Through strategic incorporation of afternoon exercise, coupled with an informed and dedicated approach, you have the tools to impact your health positively.
Take the reins and harness the transformative potential of afternoon exercise. Embrace the synergy of movement and timing in not just managing but truly living life beyond the constraints of Type 2 Diabetes.
References:
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your exercise routine or managing a health condition like Type 2 Diabetes.

Walking: A Powerful Tool Reducing Your Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
At diabeteslifebalance.com, we are dedicated to providing you with the most valuable and up-to-date information on health and wellness. In this article, we will explore the incredible benefits of walking and how it can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Recent studies have shown compelling evidence that regular walking can play a vital role in maintaining a healthy lifestyle and preventing the onset of this prevalent metabolic disorder. Join us as we delve into the details of this groundbreaking research and uncover the profound impact walking can have on your overall well-being.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from the body’s inability to utilize insulin properly. Diabetes is commonly associated with a sedentary lifestyle, poor dietary choices, obesity, and genetic factors. It affects millions of individuals worldwide and can lead to severe complications if left unmanaged. However, emerging scientific evidence suggests that a simple yet effective solution to mitigate the risk of type 2 diabetes lies in the act of walking.
The Link Between Walking and Reduced Diabetes Risk
A comprehensive study conducted by esteemed researchers has shed light on the profound relationship between walking and preventing type 2 diabetes. The study, which analyzed data from a diverse population over an extended period, found that individuals who engaged in regular walking experienced a significant reduction in their risk of developing this metabolic disorder.
The research showed that walking positively affects our health, including weight management, insulin sensitivity, cardiovascular fitness, and overall metabolic health. By engaging in moderate-intensity walking for at least 30 minutes daily, individuals can witness remarkable improvements in their overall well-being while significantly lowering their risk of type 2 diabetes.
Mechanisms Behind Walking’s Benefits
Walking offers many benefits that contribute to the prevention of type 2 diabetes. Let’s explore some of the fundamental mechanisms through which walking positively impacts our health:
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Walking enhances insulin sensitivity, allowing our cells to utilize glucose effectively. This improved sensitivity leads to better blood sugar control and reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Weight Management: Walking plays a crucial role in managing body weight. It helps burn calories, reduces excess body fat, and promotes a healthy body composition. Maintaining a healthy weight is critical in reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Cardiovascular Health: Regular walking improves cardiovascular fitness by strengthening the heart, enhancing blood circulation, and lowering blood pressure. A healthy cardiovascular system is essential for reducing the risk of developing various chronic diseases, including type 2 diabetes.
- Stress Reduction: Walking offers a natural way to alleviate stress and improve mental well-being. Chronic stress has been linked to increased blood sugar levels and insulin resistance, making stress management a crucial aspect of diabetes prevention.
Incorporating Walking into Your Routine
Now that we understand the profound benefits of walking in reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes let’s explore some practical tips to help you incorporate this healthy habit into your daily routine:
- Start Slowly: If you’re new to walking or physical activity, begin with shorter walks at a comfortable pace. Gradually increase the duration and intensity as your fitness level improves.
- Make It a Habit: Consistency is key. Aim to walk for at least 30 minutes daily, or consider breaking it into smaller sessions throughout the day if it suits your schedule better.
- Find Your Motivation: Walking with a partner, listening to music, or exploring scenic routes can help make your walks more enjoyable and encourage long-term adherence.
- Track Your Progress: Utilize fitness trackers or smartphone apps to monitor your walking progress, such as distance covered, steps taken, and calories burned. Keeping track of your achievements can motivate and help you stay on track toward your goals.
- Make it Social: Consider joining walking groups or participating in community events focused on walking. Engaging with others who share your interest in walking can provide a sense of community and encouragement to maintain your walking routine.
- Incorporate Walking into Daily Activities: Look for opportunities to walk during your daily activities. Park your car farther from your destination, take the stairs instead of the elevator, or go for short walks during your lunch breaks. Every step counts!
In conclusion, walking is a powerful tool in reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Engaging in regular walking not only improves insulin sensitivity, aids in weight management, and enhances cardiovascular health but also contributes to stress reduction and overall well-being. By making walking a part of your daily routine and adopting a proactive approach to your health, you can significantly lower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
At Diabeteslifebalance, we encourage you to prioritize your health and embrace the countless benefits of walking. Remember, every step you take brings you closer to a healthier and more vibrant life. Start walking today and pave the way for a diabetes-free future.
Please note that while walking is an effective method for reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant lifestyle changes or starting a new exercise routine, especially if you have any pre-existing health conditions.
References:
- Hawley, J. A., & Lessard, S. J. (2008). Exercise training-induced improvements in insulin action. Acta Physiologica, 192(1), 127-135.
- Jeon, C. Y., Lokken, R. P., Hu, F. B., & van Dam, R. M. (2007). Physical activity of moderate intensity and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Diabetes care, 30(3), 744-752.
- Knowler, W. C., Barrett-Connor, E., Fowler, S. E., Hamman, R. F., Lachin, J. M., Walker, E. A., & Nathan, D. M. (2002). Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. New England Journal of Medicine, 346(6), 393-403.
DiabetesLifeBalance.com is not affiliated with the mentioned articles or its website. This article is solely created to provide valuable information and promote the benefits of walking in relation to type 2 diabetes risk reduction.
Steps You Need to Take to Prevent Type II Diabetes.
The struggle against type II diabetes has never been more critical. As the rate of this condition continues to climb, it’s time to prioritize our health and wellness, starting with understanding how to reduce our risk of developing this chronic illness. We have created articles and other resources on managing diabetes and achieving balance.
Understanding Type II Diabetes
Type II diabetes is a condition where the body either does not produce enough insulin, or it resists insulin. According to the American Diabetes Association, this can lead to elevated glucose levels in the bloodstream, causing various health issues if left untreated.
Lifestyle Modifications: A Key to Prevention
Studies suggest that lifestyle modifications, such as healthy eating, maintaining a healthy weight, and regular exercise, are effective ways to prevent type II diabetes[^1^].
Eating Healthily to Regulate Blood Sugar
Creating a balanced diet is crucial for reducing the risk of type II diabetes. Opt for whole foods that are low in sugar and saturated fats, such as fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and whole grains[^2^]. Remember, moderation is key, even when it comes to healthy foods. For additional tips on building a diabetes-friendly diet, check out our guide.
Regular Exercise: More Than Just Weight Control
Engaging in regular physical activity not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also improves insulin sensitivity[^3^]. This means that your cells can use available insulin more efficiently, which helps keep your blood sugar levels in check. Even moderate exercise, like brisk walking, can make a significant difference. For exercise inspiration, visit our activity page.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Studies have shown that being overweight increases the risk of type II diabetes[^4^]. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is an excellent way to reduce this risk.
Regular Check-ups: Early Detection, Early Action
Early detection can be a critical factor in preventing the progression of type II diabetes. Regular medical check-ups and blood glucose screenings can help detect prediabetes, which often precedes type II diabetes[^5^].
The Road Ahead
Preventing type II diabetes may seem daunting, but with the right lifestyle modifications, it’s entirely possible. You can significantly reduce your risk by eating healthily, staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, and going for regular check-ups.
It’s time to embark on a healthier, balanced lifestyle journey. For more information and support, visit [https://diabeteslifebalance.com/].
Footnotes
- Mayo Clinic. (2020). Type 2 Diabetes – Symptoms and causes ↩
- Harvard School of Public Health. (2020). Diet Review: Mediterranean Diet ↩
- American Diabetes Association. (2018). Physical Activity/Exercise and Diabetes: A Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association ↩
- [CDC. (2021). Over Weight and Diabetes Risk](https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/risk-factors.html)
- American Diabetes Association. (2018). Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018.https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/41/Supplement_1/S13/30088/2-Classification-and-Diagnosis-of-Diabetes
It’s your journey, your health, and your life. The steps you take today can lead to a healthier, diabetes-free tomorrow. Remember, you’re not alone on this journey. Keep learning, stay motivated, and explore the vast resources available at Diabetes Life Balance.
Start today for a healthier tomorrow!


