You Need to Know the Role of Insulin in Diabetes Management
This article delves into the intricate relationship between diabetes and insulin, highlighting recent advancements in protein-based drugs and their potential impact on diabetes treatment. Our aim is to offer valuable insights to individuals seeking knowledge on this subject and to support them in making informed decisions about their health. To be sure, the writers at diabeteslifebalance.com are not doctors but diabetics who care about their health and share what they learn.
Diabetes: A Complex Metabolic Disorder
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Elevated blood glucose levels characterize it due to either inadequate insulin production or impaired insulin action. The condition can be classified into different types, including Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and others.
The Role of Insulin in Diabetes
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. It enables glucose to enter cells, which is utilized for energy production. In individuals with diabetes, the normal insulin function is disrupted, resulting in abnormal blood sugar levels.
Traditional Insulin Therapy
For many years, insulin therapy has been a cornerstone of diabetes management. Traditional insulin treatments involve regular injections to provide the body with the necessary insulin. These injections help regulate blood glucose levels, preventing complications of high or low blood sugar.
Advancements in Protein-Based Drugs
Recently, there have been exciting advancements in developing protein-based drugs for diabetes treatment. Researchers and pharmaceutical companies have been exploring innovative approaches to improve the efficacy and convenience of insulin therapy. One such breakthrough is the development of long-acting insulin analogs that provide sustained blood sugar control with fewer injections.
The Potential of Protein-Based Insulin Drugs
Protein-based drugs, such as insulin analogs, have shown great promise in diabetes management. These medications are designed to mimic the action of natural insulin more closely, resulting in improved glucose control and fewer adverse effects. Additionally, protein-based drugs offer enhanced convenience, allowing for less frequent dosing and potentially reducing the burden on individuals with diabetes.
The Study on Protein-Based Insulin Drugs
A recent study highlighted in an article by The Independent sheds light on the effectiveness of protein-based insulin drugs in diabetes treatment. The study, conducted by esteemed researchers in the field, examined the impact of a novel insulin analog on a cohort of individuals with Type 2 diabetes. The findings revealed significant improvements in blood sugar control and a reduction in hypoglycemic events, offering hope for those living with this condition.
In conclusion, the evolving field of diabetes management continues to witness advancements in protein-based drugs, such as insulin analogs. These medications hold great potential for improving the lives of individuals with diabetes by enhancing blood sugar control and reducing treatment complexities. The study discussed in this article further emphasizes the positive impact of protein-based insulin drugs on diabetes management. As a leading authority in the field, we are dedicated to staying at the forefront of research and providing up-to-date information to empower individuals in their journey towards better health.
Remember, managing diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that includes regular medical check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and proper medication adherence. If you have diabetes or suspect you may be at risk, we encourage you to consult a healthcare professional who can provide personalized guidance tailored to your needs.
References
- American Diabetes Association. (2021). Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. Diabetes Care, 44(Supplement 1), S1-S223. Link
- International Diabetes Federation. (2021). IDF Diabetes Atlas. 9th edition. Link
- Nathan, D. M., Genuth, S., Lachin, J., et al. (2005). The Effect of Intensive Treatment of Diabetes on the Development and Progression of Long-Term Complications in Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. New England Journal of Medicine, 329(14), 977-986. Link
Could You Be At Risk? New Reports Terrifying Estimates Regarding the Global Diabetes Epidemic.
Diabetes has emerged as a significant global health concern, with its prevalence skyrocketing over the past few decades. The impact of this chronic metabolic disorder extends beyond individuals, affecting families, communities, and healthcare systems worldwide. In this article, we delve into the alarming projections of diabetes rates and their implications for the future. By exploring the factors contributing to this epidemic, understanding the different types of diabetes, and emphasizing the importance of prevention and management, we aim to shed light on this pressing issue.
The Alarming Projections
A recent report in the Daily Mail highlights the projected rise in diabetes rates, indicating a staggering increase from 529 million cases in 2021 to an estimated 1.3 billion cases by 2050. These numbers paint a grim picture of the future, urging us to take immediate action to mitigate the impact of this epidemic. The implications are far-reaching, encompassing both individual health outcomes and the strain placed on healthcare systems worldwide.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels resulting from either insufficient insulin production or ineffective utilization of insulin. There are primarily three types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: This form of diabetes typically develops in childhood or adolescence. It occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections for life to regulate their blood sugar levels.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is the most common form, accounting for most diabetes cases globally. It usually develops in adulthood, although it increasingly affects younger individuals due to rising obesity rates and sedentary lifestyles. In type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough insulin to meet the body’s needs. Lifestyle modifications like healthy eating, regular exercise, and medication are vital to managing type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational Diabetes: Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes cause insulin resistance. While it usually resolves after childbirth, women with gestational diabetes are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Factors Contributing to the Diabetes Epidemic
Multiple factors contribute to the rising prevalence of diabetes globally. These include:
- Obesity: The increasing prevalence of obesity plays a significant role in the diabetes epidemic. Excess body weight and sedentary lifestyles contribute to insulin resistance and the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Unhealthy Diets: Diets high in processed foods, sugary beverages, and unhealthy fats contribute to weight gain and the risk of developing diabetes. A lack of nutritious food exacerbates this issue, particularly in underserved communities.
- Sedentary Lifestyles: Modern lifestyles characterized by long hours of sitting, limited physical activity, and a decline in exercise contribute to the risk of developing diabetes. Regular physical activity is crucial in preventing and managing diabetes.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing diabetes. While genetic factors alone do not cause diabetes, they can increase susceptibility when combined with environmental and lifestyle factors.
Prevention and Management Strategies
To combat the diabetes epidemic, a comprehensive approach focusing on prevention, early detection, and effective management is crucial. Here are some key strategies:
- Public Health Campaigns: Increasing awareness about diabetes risk factors, promoting healthy lifestyles, and encouraging regular screenings can significantly impact prevention and early detection.
- Healthy Eating: Emphasizing the importance of balanced, nutrient-dense diets can help prevent obesity and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Encouraging the consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean, and healthy fats while limiting processed foods and sugary beverages can contribute to diabetes prevention.
- Regular Physical Activity: Encouraging individuals to exercise regularly is crucial for diabetes prevention and management. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, promotes weight management, and enhances cardiovascular health. Aim for aerobic workouts, strength training, and flexibility exercises. You can discover the benefits of regular physical activity (afternoon and walking) for diabetes control.
- Routine Screening and Early Detection: Regular health check-ups should include screenings for diabetes risk factors, such as blood sugar levels and body mass index (BMI). Early detection allows for timely intervention and management of the condition.
- Medication and Insulin Therapy: For individuals with diabetes, appropriate medication and insulin therapy may be necessary to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. This should be done under the guidance and supervision of healthcare professionals.
- Diabetes Education and Support: Providing access to diabetes education and support programs is crucial for individuals with diabetes. These programs can offer valuable information, guidance on lifestyle modifications, and emotional support to help individuals effectively manage their condition.
- Collaboration Between Healthcare Professionals: Establishing a collaborative approach among healthcare professionals, including primary care physicians, endocrinologists, dietitians, and diabetes educators, ensures comprehensive care for individuals with diabetes. The care plan should include regular follow-ups, medication adjustments, and lifestyle counseling.
The projected rise in global diabetes rates is a cause for concern, necessitating urgent action to curb this epidemic. By understanding the different types of diabetes, addressing the factors contributing to its prevalence, and implementing effective prevention and management strategies, we can strive to mitigate the impact of this chronic condition. Through public health initiatives, education, healthy lifestyle promotion, and accessible healthcare services, we can work towards a healthier future where diabetes rates are reduced and individuals with diabetes can lead fulfilling lives. Let us join forces in combating the diabetes epidemic and prioritizing the health and well-being of our communities.

Type 2 Diabetes: How to Manage & Monitor Your Child’s Blood Sugar
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects people of all ages, including children. It occurs when the body cannot effectively use insulin or does not produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. In recent years, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in children has been on the rise, largely due to lifestyle factors such as poor diet and lack of physical activity.
In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to type 2 diabetes in children, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management. We will also discuss the importance of early detection and provide tips for parents to support their child’s overall health and well-being
1. What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar. As a result, glucose builds up in the bloodstream instead of being used for energy.
While type 2 diabetes is often associated with adults, it is increasingly diagnosed in children and adolescents. This is primarily due to lifestyle factors such as unhealthy eating habits, sedentary behavior, and excess body weight. Genetics and family history also play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes.
2. Causes of Type 2 Diabetes in Children
The exact causes of type 2 diabetes in children are not fully understood. However, several factors contribute to its development:
- Obesity: Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, increases the risk of insulin resistance.
- Unhealthy Diet: Consuming a diet high in sugar, saturated fats, and processed foods can contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary behavior and a lack of exercise reduce the body’s ability to use insulin effectively.
- Family History: Having a close family member with type 2 diabetes increases the risk.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics, and Native Americans, have a higher predisposition to type 2 diabetes.
3. Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes in Children
Recognizing the symptoms of type 2 diabetes in children is crucial for early detection and management. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent Urination: Children may need to urinate more often than usual, including nighttime bedwetting.
- Increased Thirst: Excessive thirst and constant feelings of dehydration.
- Fatigue: Children with type 2 diabetes may experience persistent fatigue and lack of energy.
- Weight Loss or Gain: Unexplained weight loss or weight gain may occur.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels can affect the eyes, causing blurred vision.
- Slow Healing: Wounds or infections may take longer to heal.
- Yeast Infections: Girls may develop frequent yeast infections.
- Darkened Skin: Certain areas of the skin, such as the neck and armpits, may appear darker than usual.
4. Diagnosing Type 2 Diabetes in Children
If you suspect that your child may have type 2 diabetes, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. The diagnosis process typically involves the following:
- Medical History: The doctor will review your child’s medical history and ask about any symptoms or risk factors.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination may be conducted to check for signs of diabetes, such as high blood pressure or darkened skin patches.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests, including fasting blood sugar levels and HbA1c tests, are used to measure blood glucose levels over a period of time.
5. Treatment Options for Children with Type 2 Diabetes
The goal of treatment for children with type 2 diabetes is to manage blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Treatment options may include:
- Lifestyle Changes: Encouraging healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, and weight management.
- Medications: In some cases, oral medications may be prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Insulin Therapy: Insulin injections or an insulin pump may be necessary if lifestyle changes and oral medications alone cannot control blood sugar levels.
6. Lifestyle Changes and Management Strategies
Managing type 2 diabetes in children requires lifestyle changes promoting overall health and well-being. Here are some important strategies:
- Healthy Eating: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit sugary foods and drinks.
- Regular Exercise: Encourage your child to engage in physical activities they enjoy, such as biking, swimming, or dancing. Aim for at least 60 minutes of exercise per day.
- Weight Management: Work with a healthcare professional to develop a weight management plan that is appropriate for your child’s age and growth.
7. Importance of Education and Support
Education and support play a vital role in managing type 2 diabetes in children. Some important aspects to consider include:
- Diabetes Education: Learn about diabetes together with your child. Teach them about blood sugar monitoring, medication management, and the importance of a healthy lifestyle.
- Support Groups: Connect with other families who have children with type 2 diabetes. Sharing experiences and tips can provide valuable support.
- School Involvement: Communicate with your child’s school to ensure they understand the condition and can provide necessary accommodations.
8. Tips for Parents and Caregivers
As a parent or caregiver of a child with type 2 diabetes, providing the necessary support is essential. Here are some tips to help you along the way:
- Be a Role Model: Adopt healthy eating habits and an active lifestyle yourself to set a positive example for your child.
- Create a Supportive Environment: Ensure your home environment promotes healthy choices by stocking nutritious foods and encouraging physical activity.
- Open Communication: Maintain open lines of communication with your child about their diabetes. Encourage them to share any concerns or challenges they may face.
- Routine Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with healthcare professionals to monitor your child’s progress and adjust treatment if needed.
9. Meal Planning and Healthy Eating Habits
Meal planning plays a crucial role in managing type 2 diabetes in children. Here are some helpful tips:
- Balanced Meals: Aim to include a variety of food groups in each meal, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- Portion Control: Teach your child about appropriate portion sizes to avoid overeating.
- Smart Snacking: Encourage healthy snacks such as fruits, vegetables, and nuts instead of sugary snacks or processed foods.
Carbohydrate Management: Monitor and manage the intake of carbohydrates, as they directly affect blood sugar levels. Choose complex carbohydrates and avoid sugary foods and beverages.
- Meal Timing: Establish regular meal times and avoid skipping meals to maintain consistent blood sugar levels.
10. Physical Activity and Exercise Recommendations
Regular physical activity is crucial for children with type 2 diabetes. Consider the following recommendations:
- Age-Appropriate Activities: Engage your child in activities they enjoy, such as biking, swimming, or team sports.
- Screen Time Limitations: Limit sedentary activities, such as excessive screen time, and encourage active play instead.
- Structured Exercise: Aim for at least 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity each day. This can be broken down into smaller sessions throughout the day.
11. Emotional Well-being and Mental Health
Living with type 2 diabetes can have emotional and mental health implications for children. Here’s how you can support their well-being:
- Open Communication: Create a safe space for your child to express their feelings and concerns about their condition.
- Positive Reinforcement: Recognize and celebrate your child’s efforts in managing their diabetes and making healthy choices.
- Stress Management: Teach your child stress management techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or engaging in relaxing activities.
12. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial to manage type 2 diabetes in children effectively. Consider the following:
- Blood Glucose Testing: Work with your healthcare team to determine how frequently your child should test their blood sugar levels.
- Target Ranges: Understand the target blood sugar range for your child and take appropriate actions based on the results.
- Record Keeping: Maintain a log of blood sugar readings to identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
13. Medications and Insulin Therapy
In some cases, children with type 2 diabetes may require medications or insulin therapy to manage their condition. Here’s what you need to know:
- Oral Medications: Some children may be prescribed oral medications, such as metformin, to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Insulin Therapy: If oral medications are not sufficient, your child may need insulin therapy. This can be administered through injections or an insulin pump.
- Careful Monitoring: Regularly monitor your child’s response to medications or insulin therapy and consult with healthcare professionals for any necessary adjustments.
14. Potential Complications of Type 2 Diabetes in Children
While managing type 2 diabetes is crucial, it’s also important to be aware of potential complications. These can include:
- Heart Disease: Children with type 2 diabetes are at a higher risk of developing heart disease later in life.
- Kidney Disease: Poorly controlled blood sugar levels can lead to kidney damage over time.
- Eye Problems: Diabetes can affect the eyes and increase the risk of conditions such as retinopathy or cataracts.
- Nerve Damage: Long-term high blood sugar levels can cause nerve damage, leading to issues such as numbness or tingling in the hands and feet.
Managing type 2 diabetes in children requires a comprehensive approach that focuses on lifestyle changes, education, support, and medical intervention when necessary. By promoting healthy habits, monitoring blood sugar levels, and providing emotional support, parents and caregivers can help their child live a fulfilling life while effectively managing their condition.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Can type 2 diabetes in children be prevented?
Type 2 diabetes can sometimes be prevented or delayed by implementing healthy lifestyle habits from an early age. This includes promoting a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Is type 2 diabetes reversible in children?
While type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition, lifestyle changes and proper management can help control blood sugar levels effectively. With early intervention and consistent adherence to a healthy lifestyle, some children may be able to achieve normal blood sugar levels and reduce the need for medication or insulin therapy. - Can my child with type 2 diabetes still enjoy treats and desserts?
Yes, your child can still enjoy treats and desserts in moderation. Teaching them about portion control and making healthier choices, such as opting for low-sugar or sugar-free alternatives, is essential. Incorporating treats into a balanced meal plan can help them manage their blood sugar levels effectively. - Should my child with type 2 diabetes participate in physical activities and sports?
Absolutely! Physical activity is highly beneficial for children with type 2 diabetes. Regular exercise and sports can help improve insulin sensitivity, promote weight management, and enhance overall well-being. However, it is essential to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure appropriate precautions are taken to prevent any complications. - How can I support my child emotionally in dealing with type 2 diabetes?
Supporting your child emotionally is crucial in their diabetes management. Listen to their concerns, provide reassurance, and encourage open communication. Help them build a support network by connecting with other families facing similar challenges. Consider involving them in decision-making regarding their diabetes management to empower them and foster a sense of control.
Living with Diabetes: Managing Your Health and Embracing a Balanced Lifestyle
Living with diabetes requires proactive management and a balanced approach to maintaining your health. By incorporating key strategies into your daily routine, such as following a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and effectively managing medications, you can take control of your diabetes and lead a fulfilling life. This article will explore practical tips and insights for living with diabetes, empowering you to embrace a balanced lifestyle while effectively managing your condition.
Diet plays a crucial role in diabetes management. Focus on consuming various nutrient-dense foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid or limit foods high in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium. Be mindful of portion sizes and consult a registered dietitian specializing in diabetes nutrition to create a personalized meal plan that suits your needs.
Regular physical activity is essential for individuals living with diabetes. Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote cardiovascular health. Aim for a combination of aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, and strength training exercises to build muscle mass. Consult your healthcare provider before starting any exercise regimen and gradually increase your activity level.
Medication management is a crucial aspect of diabetes care. Taking prescribed medications as directed and monitoring blood glucose levels regularly is essential. Understand your medications’ purpose and potential side effects and communicate any concerns or difficulties to your healthcare provider. Additionally, ensure you have a sufficient supply of medication and develop a routine to help you remember to take your medications on time.
In addition to diet, exercise, and medication management, self-care practices are vital for managing diabetes effectively. Stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies, can help reduce stress levels and support overall well-being. Prioritize quality sleep, maintain regular check-ups with your healthcare team, and stay educated about diabetes management through reliable sources.
Living with diabetes may present challenges, but you can lead a fulfilling life with the right mindset and support. Surround yourself with a strong support system of family, friends, and healthcare professionals who understand and encourage your diabetes management goals. Stay positive, set achievable targets, and celebrate small victories.
In conclusion, living with diabetes requires a holistic approach that encompasses diet, exercise, medication management, and self-care practices. By adopting a balanced lifestyle and incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can effectively manage your diabetes and enjoy an active, fulfilling life. Remember, with proper management and support, living well with diabetes is entirely possible.
Cola and Other soda’s impact on Persons with Diabetes
Regular cola, a beverage that may seem innocuous to some, harbors hidden dangers for individuals with diabetes. The abundance of sugar within its fizzy depths presents formidable health hazards that cannot be ignored. In this composition, we embark on an odyssey through the perilous terrain of consuming regular cola for those afflicted by this chronic ailment. We unearth the potential perils intertwined with this saccharine libation, deliberate upon the merits of diminishing soda consumption, and offer sagacious counsel on ameliorating this predicament by exploring alternative avenues.
Foremost among the concerns plaguing diabetics who dare to indulge in regular cola is its profound impact on the delicate equilibrium of blood glucose levels. This seemingly innocent beverage, with its excess of added sugars—often in the form of high fructose corn syrup—poses a perilous threat. It swiftly raises blood glucose levels to unprecedented heights, exacerbating the struggles of individuals grappling to maintain balance. Egregiously elevated blood sugar levels engender many debilitating symptoms, from an unquenchable thirst to overwhelming fatigue and even a disconcerting blurring of vision.
Unsurprisingly, the relentless elevation of blood sugar levels precipitates a litany of long-term complications, indubitably exacerbating the tribulations faced by those with diabetes. Prolonged exposure to the perils of exorbitant sugar levels can inflict grievous damage upon blood vessels and nerves, setting the stage for heightened susceptibility to afflictions such as heart disease, renal maladies, and neuropathy. Furthermore, wanton indulgence in copious amounts of sugar-laden beverages invariably contributes to undesirable weight gain, amplifying the risk factors associated with diabetes and further complicating its management.
However, a palpable benefit can be gained by reducing the prodigious consumption of soda for individuals grappling with diabetes. By judiciously curtailing regular cola intake, we can regain mastery over blood sugar levels while diminishing the risk of debilitating complications. Minor adjustments to our dietary predilections possess an astonishing capacity to engender immense impact on our overall well-being. It’s important to note that we need not adopt a draconian stance, seeking to eradicate soda entirely. Instead, a more sagacious approach necessitates a gradual reduction in consumption over time, allowing for a sustainable transition that mitigates the gnawing sensation of deprivation often associated with abrupt dietary alterations.
Let us inaugurate the arduous journey towards diminishing the consumption of cola by contemplating the following stratagems:
- Delicate dilution: Embark upon a voyage of incremental reduction in cola quantity within your glass and supplement it with the elixir of life itself—water. This crafty maneuver dampens overall sugar intake while ensuring taste familiarity remains intact.
- Unveiling sugar-free alternatives: Consider the veritable cornucopia of diet or zero-sugar colas that present themselves as viable options. These variants artfully employ artificial sweeteners as surrogates for their sugar-laden brethren, resulting in a marginal impact on blood sugar levels. However, we must acknowledge that some individuals may encounter digestive tribulations or harbor reservations about the long-term consequences entwined with the consumption of artificial sweeteners.
- Venture forth into the uncharted realm of healthier alternatives: Bid farewell to regular cola and forge ahead, embracing the tantalizing allure of beverages such as effervescent sparkling water, tantalizingly infused water, or soothing herbal tea. These exquisite choices serve as commendable substitutes that curtail sugar intake and bestow the gift of hydration without the harmful repercussions of excessive sugar consumption.
However, it is paramount to remember that consulting with a reputable healthcare professional or a registered dietitian is essential before embarking upon any momentous metamorphosis in one’s dietary regimen, particularly if one grapples with the relentless clutches of diabetes. These esteemed experts are poised to proffer personalized guidance tailored to one’s unique circumstances and medical history.
The dire consequences of drinking regular cola cannot be overstated for individuals burdened with diabetes. The conspicuous profusion of sugar ensconced within its effervescent confines precipitates perilous surges in blood sugar levels, augments the risk of debilitating complications, and engenders the insidious encroachment of unwelcome weight gain. By gradually ameliorating soda consumption and embarking upon an exploration of more salubrious alternatives, individuals grappling with diabetes may embark upon an odyssey defined by infinitesimal yet profoundly meaningful strides toward the management of their condition and the enhancement of overall well-being.
You possess the power to make a positive change in your life. You can reclaim your health and well-being by taking control of your soda consumption. Say farewell to the lurking perils of regular cola and embrace the path of moderation and healthier alternatives. Your journey toward a better future begins today.
Enjoy a variety of vegetables for healthy living to help your diabetes
Providing our bodies with nutrient-rich food, mainly fruits and vegetables, is essential for our health and well-being. Nevertheless, many struggle to integrate these nutritious foods into their daily meals. However, do not despair; nourishing yourself and your loved ones with healthy and appetizing dishes can be more effortless than you presume.
Venturing into the produce section of your nearby supermarket can lead to delightful culinary creations. The leading grocery chains offer a vast range of fruits and vegetables from around the globe. By experimenting with new and exceptional produce, you incorporate delightful flavors into your meals and enrich your nutritional consumption. The monotony in a healthy diet can be tiring, resulting in a lack of incentive to fuel our bodies. Hence, it is crucial to break this dietary ennui to attain longevity and triumph in a healthy eating plan.
Why not step out of your comfort zone by trying collard greens, asparagus, or kale? Discovering new and exquisite produce can simultaneously benefit your physical well-being. Leafy vegetables such as spinach, broccoli, and kale comprise vital vitamins, minerals, and micronutrients. A diverse selection of fresh, frozen, and canned varieties can assist in broadening your vegetable options, especially during the off-season. Fresh fruits and vegetables offer diverse flavors, shades, and textures that enable you to consume a spectrum of essential nutrients. For instance, yellow and orange produce typically have high beta-carotene content, while green leafy vegetables offer significant calcium and other critical nutrients. Incorporating bright yellow peppers or vivacious orange carrot slivers can enhance your plain green salad and elevate it to a more vibrant and nutritious level.
Several groups within modern society believe that vitamin and mineral supplements can rectify a poor diet. Despite the continued popularity of these products, it is imperative to recognize that whole foods contain numerous minerals, trace elements, and other micronutrients. Consequently, even the most comprehensive supplement cannot adequately substitute a well-balanced diet.
Vitamin and mineral supplements cost more and are less tasty than fruits and vegetables. When transitioning to a more health-conscious lifestyle, you must become well-informed about proper eating habits and determine the optimal fruits and vegetables for your palate. A balanced diet that you can sustain indefinitely is the most effective diet. Prioritizing the freshest fruits and vegetables enhances the taste, reduces expenses, and amplifies nutritional value. Opting for various in-season produce each week establishes the foundation for wholesome, diverse meals. Nevertheless, your preferred produce may not always be available, requiring the occasional substitution with canned and frozen alternatives. When selecting canned fruits, avoid those preserved in syrup and opt for those conserved in fruit juice or water, as they contain less sugar.
Incorporating fresh fruit, such as apple segments, mandarin oranges, nectarines, and the like, can elevate plain salads to newfound heights of flavor and interest. Combining fruits and vegetables optimizes nutritional benefits and provides an exciting culinary experience. So, start now and explore new vegetable and fruit produce and relish the advantages of a healthy and diverse diet.

One way to create wonderful meals that are healthier than ever is to take a stroll through the produce section of your local grocery store. Most major grocery store chains have huge produce sections, containing a wonderful variety of fruits and vegetables from all corners of the world.
Trying a variety of different fruits and vegetables is a great way to keep your meals interesting and exciting in addition to nutritious. It is all too easy to become bored when trying to follow a healthy diet, and boredom can lead people to abandon their healthy habits. Avoiding diet burnout is important to the long term survival of even the most sensible eating plan.
So if you’ve never had vegetables like collard greens, asparagus or kale before, why not give them a try. Not only can trying new things allow you to make great new discoveries, but it can increase your level of fitness as well. Leafy green vegetables like spinach, broccoli and kale are rich sources of many important vitamins, minerals and other micronutrients.
Another great way to increase the variety of vegetables you enjoy is to combine fresh, frozen and canned vegetables. While fresh vegetables are generally better and healthier, frozen and canned vegetables can be great alternatives for when the fresh varieties are out of season.
One of the best things about fresh fruits and vegetables is the great variety of flavors, colors and textures available. Eating a variety of different colored vegetables and fruits does much more than provide much needed variety. It also provides a great variety of nutrients. For instance, yellow and orange fruits and vegetables tend to be very high in beta carotene, while green leafy vegetables are often great sources of calcium and other important nutrients. So why not spice up your plain old green salad with a splash of color in the form of yellow peppers or orange carrot slices?
Many people wrongly think that they can make up for a crappy diet by using vitamin and mineral supplements. This mistaken belief is apparently very widespread, since sales of these supplements continue to break records. When considering vitamin and mineral supplements, however, it is important to remember that foods contain many different minerals, trace elements and other micronutrients. That means that for every nutrient that has been discovered and synthesized, there may be ten, twenty or more of these micronutrients that have yet to be fully understood. That is why no vitamin supplement, no matter how complete, can truly replace a healthy, balanced diet.
In addition, vitamin and mineral supplements are quite a bit more expensive than a good selection of vegetables and fruits, and not nearly as tasty.
One of the best ways to start eating a healthy diet is to choose the freshest fruits and vegetables. Not only do fresh fruits and vegetables taste better, but they are less expensive and more nutritious as well. Choosing a variety of in season fruits and vegetables every week is a great way to enjoy healthy and varied meals.
Of course your favorite fruits and vegetables will not always be in season, so it will sometimes be necessary to supplement those fresh fruits and vegetables with canned and frozen varieties. When choosing canned fruits, try to avoid those packed in syrup; choose canned fruits packed in fruit juice or water instead. They will be healthier and contain less sugar.
Adding fresh fruit, such as apple slices, mandarin oranges, nectarines and the like is a great way to make plain salads more interesting and more delicious. Combining fruits and vegetables is a great way to enhance your nutrition as well.
How Does Insulin Affect Us
The food we consume significantly can and does impact our body’s functioning, and blood glucose levels are no exception. Understanding how different foods affect our blood sugar is crucial in managing and preventing certain health conditions. This is where the glycemic index comes in, as it serves as a tool for comprehending the efficacy of foods in regulating blood glucose levels. But what is the glycemic index, and how does it impact our health? Let’s delve deeper into this topic and explore the importance of the glycemic index in maintaining a healthy body.
Experts have acknowledged the efficaciousness of low glycemic index regimens in advancing human health. This is because low glycemic index victuals are subjected to a more gradual decomposition into glucose, resulting in diminished insulin secretion. While the investigation into this matter is continuous, the immoderate intake of high glycemic index comestibles and fast food that are high in lipids remains a principal source of apprehension. The Glycemic Index is an innovative arrangement for classifying carbohydrates based on their instant effects on blood glucose levels. Carbohydrates that are swiftly transformed into glucose during digestion, leading to a sudden increase in glucose levels, are attributed high glycemic index values. Carbohydrates that require more time to disintegrate are awarded intermediate or low glycemic index values. The glycemic index is a pivotal instrument for regulating blood glucose levels, especially for those who are vulnerable to developing diabetes and other persistent ailments. By adhering to a low glycemic index diet, individuals can circumvent the health dangers associated with high blood glucose levels, insulin resistance, and corpulence. Although investigation is ongoing, it is apparent that consuming high glycemic index foods and fatty fast food should be circumvented, while low glycemic index foods should be assimilated into a wholesome and balanced diet. By giving priority to low glycemic index foods, we can adopt preventive measures to sustain optimal health and well-being.
So we can see that the glycemic index is an essential tool in managing blood glucose levels, especially for people at risk of diabetes and other chronic conditions. By consuming a low glycemic index diet, people can avoid the health risks of high blood glucose levels, insulin resistance, and obesity. Although research is ongoing, it is clear that high-glycemic-index foods and fast foods high in fat should be avoided, and low-glycemic-index foods should be incorporated into a healthy and balanced diet. By prioritizing low-glycemic-index foods, we can take proactive measures to maintain optimal health and well-being.
References and studies that support the information presented in the article:
The Glycemic Index: Physiological Mechanisms Relating to Obesity, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Disease (Journal of the American Medical Association): https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/191554
Glycemic Index, Glycemic Load, and Chronic Disease Risk–A Meta-analysis of Observational Studies (The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition): https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/87/3/627/4633375
Glycemic Index and Insulin Sensitivity (The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition): https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/76/1/274S/4677495
Glycemic Index and Insulin Resistance: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials (Diabetes Care): https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/33/1/166
Carbohydrate Quality and Human Health: A Series of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (The Lancet): https://www.thelancet.com/series/food-nutrition-health
Four Types Of Diabetes! Which Are You?
Results from the body’s failure to produce insulin, the hormone that unlocks the cells of the body, allowing glucose to enter and fuel them. It is estimated that 5-10% of Americans who are diagnosed with diabetes have type 1 diabetes.
Having type 1 diabetes increases your risk for many serious complications. Some complications of type 1 diabetes include: heart disease (cardiovascular disease), blindness (retinopathy), nerve damage (neuropathy), and kidney …
Type 1 diabetes
Results from the body’s failure to produce insulin, the hormone that unlocks the cells of the body, allowing glucose to enter and fuel them. It is estimated that 5-10% of Americans who are diagnosed with diabetes have type 1 diabetes.
Having type 1 diabetes increases your risk for many serious complications. Some complications of type 1 diabetes include: heart disease (cardiovascular disease), blindness (retinopathy), nerve damage (neuropathy), and kidney damage (nephropathy).
Type 2 diabetes
Results from insulin resistance (a condition in which the body fails to properly use insulin), combined with relative insulin deficiency. Most Americans who are diagnosed with diabetes have type 2 diabetes.
Having type 2 diabetes increases your risk for many serious complications. Some complications of type 2 diabetes include: heart disease (cardiovascular disease), blindness (retinopathy), nerve damage (neuropathy), and kidney damage (nephropathy). Learn more about these complications and how to cope with them.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes affects about 4% of all pregnant women – about 135,000 cases in the United States each year.
Because gestational diabetes can hurt you and your baby, you need to start treatment quickly. Treatment for gestational diabetes aims to keep blood glucose levels equal to those of pregnant women who don’t have gestational diabetes. Treatment for gestational diabetes always includes special meal plans and scheduled physical activity. It may also include daily blood glucose testing and insulin injections. You will need help from your doctor, nurse educator, and other members of your health care team so that your treatment for gestational diabetes can be changed as needed.
For the mother-to-be, treatment for gestational diabetes helps lower the risk of a cesarean section birth that very large babies may require. Sticking with your treatment for gestational diabetes will give you a healthy pregnancy and birth, and may help your baby avoid future poor health. (see Diabetes Symptoms)
Pre-diabetes
Pre-diabetes is a condition that occurs when a person’s blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough for a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. There are 41 million Americans who have pre-diabetes, in addition to the 20.8 million with diabetes.
Is There Self Test For Diabetes?
Sixteen million Americans have diabetes, yet many are not aware of it. African Americans, Hispanics and Native Americans have a higher rate of developing diabetes during their lifetime. Diabetes has potential long term complications that can affect the kidneys, eyes, heart, blood vessels and nerves. A number of pages on this web site are devoted to the prevention and treatment of the complications of diabetes. (see Diabetes Symptoms)
Sixteen million Americans have diabetes, yet many are not aware of it. African Americans, Hispanics and Native Americans have a higher rate of developing diabetes during their lifetime. Diabetes has potential long term complications that can affect the kidneys, eyes, heart, blood vessels and nerves. A number of pages on this web site are devoted to the prevention and treatment of the complications of diabetes. (see Diabetes Symptoms)
In diagnosing diabetes, physicians primarily depend upon the results of specific glucose tests. However, test results are just part of the information that goes into the diagnosis of diabetes. Doctors also take into account your physical exam, presence or absence of symptoms, and medical history. Some people who are significantly ill will have transient problems with elevated blood sugars which will then return to normal after the illness has resolved. Also, some medications may alter your blood glucose levels (most commonly steroids and certain diuretics (water pills)).
The TWO main tests used to measure the presence of blood sugar problems are:
1. Direct measurement of glucose levels in the blood during an overnight fast
2. Measurement of the body’s ability to appropriately handle the excess sugar presented after drinking a high glucose drink.
Self Testing Methods
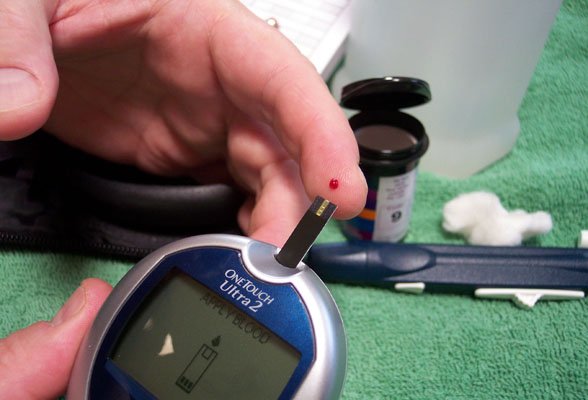
Regular self-testing of your blood sugar tells you how well your combination of diet, exercise, and medication are working. Tests are usually done before meals and at bedtime. More frequent testing may be needed when you are sick or under stress.
A device called a Glucometer can provide an exact blood sugar reading. There are different types of devices. Usually, you prick your finger with a small needle called a lancet, which gives you a tiny drop of blood. You place the blood on a test strip, and put the strip into the device. Results are available within 30 to 45 seconds.
A health care provider or diabetes educator will help set up an appropriate testing schedule for you. You will also be taught how to respond to different ranges of glucose values obtained when you self-test.
The results of the test can be used to adjust meals, activity, or medications to keep blood sugar levels in an appropriate range. Testing provides valuable information for the health care provider and identifies high and low blood sugar levels before serious problems develop. Accurate record keeping of test results will help you and your health care provide plan how to best control your diabetes. There are 20.8 million children and adults in the US with diabetes, and nearly one-third of them (or 6.2 million people) do not know it!


