You Need to Know the Role of Insulin in Diabetes Management
This article delves into the intricate relationship between diabetes and insulin, highlighting recent advancements in protein-based drugs and their potential impact on diabetes treatment. Our aim is to offer valuable insights to individuals seeking knowledge on this subject and to support them in making informed decisions about their health. To be sure, the writers at diabeteslifebalance.com are not doctors but diabetics who care about their health and share what they learn.
Diabetes: A Complex Metabolic Disorder
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Elevated blood glucose levels characterize it due to either inadequate insulin production or impaired insulin action. The condition can be classified into different types, including Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and others.
The Role of Insulin in Diabetes
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. It enables glucose to enter cells, which is utilized for energy production. In individuals with diabetes, the normal insulin function is disrupted, resulting in abnormal blood sugar levels.
Traditional Insulin Therapy
For many years, insulin therapy has been a cornerstone of diabetes management. Traditional insulin treatments involve regular injections to provide the body with the necessary insulin. These injections help regulate blood glucose levels, preventing complications of high or low blood sugar.
Advancements in Protein-Based Drugs
Recently, there have been exciting advancements in developing protein-based drugs for diabetes treatment. Researchers and pharmaceutical companies have been exploring innovative approaches to improve the efficacy and convenience of insulin therapy. One such breakthrough is the development of long-acting insulin analogs that provide sustained blood sugar control with fewer injections.
The Potential of Protein-Based Insulin Drugs
Protein-based drugs, such as insulin analogs, have shown great promise in diabetes management. These medications are designed to mimic the action of natural insulin more closely, resulting in improved glucose control and fewer adverse effects. Additionally, protein-based drugs offer enhanced convenience, allowing for less frequent dosing and potentially reducing the burden on individuals with diabetes.
The Study on Protein-Based Insulin Drugs
A recent study highlighted in an article by The Independent sheds light on the effectiveness of protein-based insulin drugs in diabetes treatment. The study, conducted by esteemed researchers in the field, examined the impact of a novel insulin analog on a cohort of individuals with Type 2 diabetes. The findings revealed significant improvements in blood sugar control and a reduction in hypoglycemic events, offering hope for those living with this condition.
In conclusion, the evolving field of diabetes management continues to witness advancements in protein-based drugs, such as insulin analogs. These medications hold great potential for improving the lives of individuals with diabetes by enhancing blood sugar control and reducing treatment complexities. The study discussed in this article further emphasizes the positive impact of protein-based insulin drugs on diabetes management. As a leading authority in the field, we are dedicated to staying at the forefront of research and providing up-to-date information to empower individuals in their journey towards better health.
Remember, managing diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that includes regular medical check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and proper medication adherence. If you have diabetes or suspect you may be at risk, we encourage you to consult a healthcare professional who can provide personalized guidance tailored to your needs.
References
- American Diabetes Association. (2021). Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. Diabetes Care, 44(Supplement 1), S1-S223. Link
- International Diabetes Federation. (2021). IDF Diabetes Atlas. 9th edition. Link
- Nathan, D. M., Genuth, S., Lachin, J., et al. (2005). The Effect of Intensive Treatment of Diabetes on the Development and Progression of Long-Term Complications in Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. New England Journal of Medicine, 329(14), 977-986. Link
What You Need to Do for Optimal Health with Diabetes
Living with diabetes can be a challenging journey filled with ups and downs. It requires careful management, lifestyle adjustments, and a deep understanding of the condition. This article will explore the various aspects of living with diabetes, providing valuable insights, practical tips, and expert advice to help you effectively manage your health. Whether you have recently been diagnosed or have been living with diabetes for a while, this article supports your path to optimal well-being.
Living with Diabetes: Understanding the Condition
Living with diabetes means navigating a chronic condition that affects how your body regulates blood sugar or glucose. Diabetes occurs when the pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes), or the body doesn’t effectively use its insulin (Type 2 diabetes). Both types require lifelong management and can lead to serious health complications if not properly addressed.
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes, also known as insulin-dependent diabetes, is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This results in a lack of insulin, crucial for moving glucose into the body’s cells for energy. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes require insulin injections or an insulin pump to manage their blood sugar levels.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes, the most common form of diabetes, occurs when the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. This type of diabetes is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, sedentary behavior, and poor dietary choices. Managing Type 2 diabetes typically involves a combination of healthy eating, regular physical activity, oral medications, and, in some cases, insulin therapy.
The Impact of Diabetes on Daily Life
Living with diabetes requires constant vigilance and self-care. The condition affects various aspects of daily life, including diet, exercise, medication management, and emotional well-being. It’s essential to understand the impact diabetes can have on different areas of your life to manage the condition and maintain overall health effectively.
Managing Your Diabetes: Practical Tips and Strategies
Living with diabetes involves making informed choices and implementing strategies that promote stable blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications. Here are some practical tips to help you effectively manage your diabetes and lead a healthy lifestyle:
1. Develop a Balanced Meal Plan
Creating a balanced meal plan is crucial for managing diabetes. Focus on consuming various nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid or limit the intake of sugary beverages, processed foods, and foods high in saturated and trans fats. Additionally, pay attention to portion sizes and the timing of your meals to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
2. Regular Physical Activity: Get Moving!
Engaging in regular physical activity offers numerous benefits for individuals with diabetes. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, manage weight, reduce stress, and boost cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week and strength training exercises. Consult your healthcare team to determine an exercise plan suitable for your needs and abilities.
3. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
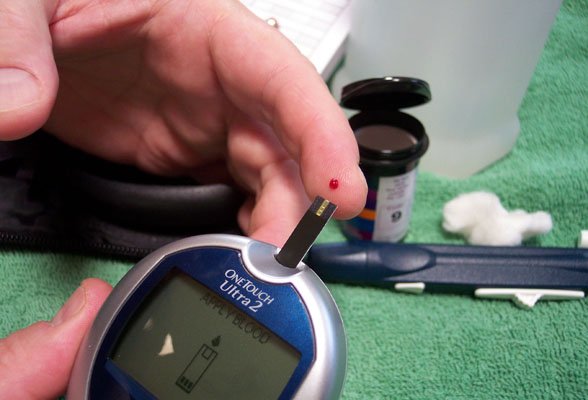
Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes effectively. Use a blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring system to keep track of your levels throughout the day. This information will help you make informed diet, physical activity, and medication management decisions. Share your records with your healthcare team to identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
4. Medication Management: Stick to Your Plan
If you’re prescribed medication to manage your diabetes, it’s crucial to adhere to your prescribed treatment plan. Take your medication as directed by your healthcare provider and be diligent about maintaining a consistent schedule. Some medications may need to be taken with meals, while others require specific timing. It’s essential to understand the purpose and potential side effects of your medications, as well as any precautions or interactions to be aware of. If you have any concerns or questions about your medication regimen, consult with your healthcare team for guidance.
5. Stay Hydrated and Limit Alcohol Consumption
Proper hydration is important for everyone, but it holds particular significance for individuals living with diabetes. Drinking an adequate amount of water helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels and supports overall well-being. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water per day and adjust your intake based on factors such as activity level, weather conditions, and individual needs.
When it comes to alcohol consumption, moderation is key. Alcohol can interfere with blood sugar control and may cause fluctuations in glucose levels. It’s advisable to limit your alcohol intake and consume alcoholic beverages in moderation, if at all. Remember to monitor your blood sugar levels closely and be aware of how alcohol affects your body.
6. Stress Management: Prioritize Self-Care
Stress can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels and overall health. Managing stress is an important aspect of diabetes care. Find healthy ways to cope with stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in hobbies, connecting with loved ones, or seeking support from a mental health professional. Prioritizing self-care and making time for activities that bring you joy and relaxation can help reduce stress levels and promote overall well-being.
7. Get Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups and screenings are essential for individuals living with diabetes. These appointments allow your healthcare team to monitor your overall health, assess your blood sugar control, and screen for any potential complications. Make sure to schedule routine visits with your primary care physician, endocrinologist, ophthalmologist, and any other specialists recommended by your healthcare team. These proactive measures can help detect and address any health concerns promptly.
8. Educate Yourself and Stay Informed
Knowledge is power when it comes to managing diabetes. Take the initiative to educate yourself about the condition, its management, and the latest advancements in diabetes care. Stay updated on new research, treatment options, and self-care strategies. Reliable sources such as reputable websites, medical journals, and diabetes organizations can provide valuable information. However, consulting with your healthcare team before implementing any changes to your treatment plan or lifestyle is essential.
9. Connect with Support Networks
Living with diabetes can sometimes feel overwhelming, but you don’t have to face it alone. Reach out to support networks and connect with others living with diabetes. Join local support groups, participate in online forums or communities, or consider attending diabetes education classes. Sharing experiences, tips, and emotional support with others who understand your journey can be immensely beneficial and empowering.
10. Embrace Technology
Technology has revolutionized diabetes management, offering various tools and devices to simplify and enhance the process. Consider incorporating technological advancements into your diabetes care routine. Continuous glucose monitoring systems, insulin pumps, smartphone apps for tracking blood sugar levels and medications, and digital platforms for connecting with healthcare providers are just a few examples of how technology can support your diabetes management efforts.
11. Take Care of Your Feet
Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing foot problems due to poor circulation and nerve damage. To protect your feet, practice good foot hygiene, inspect them regularly for any cuts, sores, or signs of infection, and wear comfortable shoes that provide proper support and fit well.
12. Prioritize Dental Care
Oral health is closely linked to overall health; individuals with diabetes are more prone to gum disease and other dental issues. Make sure to maintain good oral hygiene by brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing regularly, and scheduling regular dental check-ups. Inform your dentist about your diabetes diagnosis and work together to develop a comprehensive dental care plan that suits your needs.
13. Traveling with Diabetes
Traveling can pose unique challenges for individuals with diabetes, but proper planning and preparation can be an enjoyable experience. When traveling, ensure you have ample medication and supplies to last the duration of your trip, including extra in case of unforeseen circumstances. Carry a medical ID bracelet or card that identifies you as a person with diabetes, and familiarize yourself with the healthcare resources available at your destination. Consult your healthcare provider before traveling to discuss any specific precautions or adjustments to your treatment plan.
14. Handling Sick Days
Illness or infection can affect blood sugar levels and require special attention when you have diabetes. It’s important to have a sick day plan in place. Make sure to stay hydrated, continue taking your medication or insulin as directed, and monitor your blood sugar levels more frequently. Reach out to your healthcare team for guidance on adjusting your medication doses, if necessary. If your illness persists or worsens, seek medical attention promptly.
15. Pregnancy and Diabetes
Managing diabetes during pregnancy requires careful planning and monitoring. If you have diabetes and are planning to conceive or are already pregnant, working closely with your healthcare team to ensure optimal blood sugar control is essential. Regular prenatal care, proper nutrition, regular exercise, and close monitoring of blood sugar levels are crucial for a healthy pregnancy and to reduce the risk of complications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some common questions about living with diabetes, with simple and concise answers:
Q1: Can diabetes be reversed? A1: While Type 2 diabetes can sometimes be managed or even reversed through lifestyle changes such as weight loss, healthy eating, and increased physical activity, Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition that cannot be reversed.
Q2: What are the long-term complications of diabetes? A2: Long-term complications of diabetes can include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, eye problems, and foot problems. However, the risk of complications can be reduced with proper management and control of blood sugar levels.
Q3: Can I still enjoy my favorite foods with diabetes? A3: Yes, you can still enjoy a wide variety of foods with diabetes. The key is moderation, portion control, and making healthier choices. Working with a registered dietitian can help you create a balanced meal plan incorporating your favorite foods while managing your blood sugar levels.
Q4: Is it safe to exercise with diabetes? A4: Yes, exercise is generally safe and beneficial for individuals with diabetes. However, it’s important to consult your healthcare team before starting or changing your exercise routine, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Q5: Can stress affect my blood sugar levels? A5: Yes, stress can affect blood sugar levels. When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones that can cause your blood sugar to rise. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, relaxation techniques, or seeking support, is important for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Q6: Can I drink alcohol if I have diabetes? A6: Moderate alcohol consumption may be acceptable for some individuals with diabetes. However, alcohol can affect blood sugar control, so monitoring your levels and drinking in moderation is crucial. It’s advisable to consult with your healthcare team to determine
Q6: Can I drink alcohol if I have diabetes? A6: Moderate alcohol consumption may be acceptable for some individuals with diabetes. However, alcohol can affect blood sugar control, so monitoring your levels and drinking in moderation is crucial. It’s advisable to consult with your healthcare team to determine if alcohol is safe for you and to understand any potential interactions with your medications.
Living with diabetes requires commitment, education, and ongoing support. By implementing healthy lifestyle choices, closely monitoring blood sugar levels, adhering to medication regimens, and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their condition and lead fulfilling lives. Remember, you are not alone on this journey. Connect with support networks, stay informed, and prioritize self-care to navigate the challenges and embrace the possibilities of living with diabetes.
Incorporating these strategies into your daily routine can help you maintain stable blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve your overall quality of life. Remember, managing diabetes is a lifelong journey, and adapting and adjusting along the way is essential. Stay proactive, ask questions, and seek your support to thrive with diabetes.
Could You Be At Risk? New Reports Terrifying Estimates Regarding the Global Diabetes Epidemic.
Diabetes has emerged as a significant global health concern, with its prevalence skyrocketing over the past few decades. The impact of this chronic metabolic disorder extends beyond individuals, affecting families, communities, and healthcare systems worldwide. In this article, we delve into the alarming projections of diabetes rates and their implications for the future. By exploring the factors contributing to this epidemic, understanding the different types of diabetes, and emphasizing the importance of prevention and management, we aim to shed light on this pressing issue.
The Alarming Projections
A recent report in the Daily Mail highlights the projected rise in diabetes rates, indicating a staggering increase from 529 million cases in 2021 to an estimated 1.3 billion cases by 2050. These numbers paint a grim picture of the future, urging us to take immediate action to mitigate the impact of this epidemic. The implications are far-reaching, encompassing both individual health outcomes and the strain placed on healthcare systems worldwide.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels resulting from either insufficient insulin production or ineffective utilization of insulin. There are primarily three types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: This form of diabetes typically develops in childhood or adolescence. It occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections for life to regulate their blood sugar levels.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is the most common form, accounting for most diabetes cases globally. It usually develops in adulthood, although it increasingly affects younger individuals due to rising obesity rates and sedentary lifestyles. In type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough insulin to meet the body’s needs. Lifestyle modifications like healthy eating, regular exercise, and medication are vital to managing type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational Diabetes: Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes cause insulin resistance. While it usually resolves after childbirth, women with gestational diabetes are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Factors Contributing to the Diabetes Epidemic
Multiple factors contribute to the rising prevalence of diabetes globally. These include:
- Obesity: The increasing prevalence of obesity plays a significant role in the diabetes epidemic. Excess body weight and sedentary lifestyles contribute to insulin resistance and the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Unhealthy Diets: Diets high in processed foods, sugary beverages, and unhealthy fats contribute to weight gain and the risk of developing diabetes. A lack of nutritious food exacerbates this issue, particularly in underserved communities.
- Sedentary Lifestyles: Modern lifestyles characterized by long hours of sitting, limited physical activity, and a decline in exercise contribute to the risk of developing diabetes. Regular physical activity is crucial in preventing and managing diabetes.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing diabetes. While genetic factors alone do not cause diabetes, they can increase susceptibility when combined with environmental and lifestyle factors.
Prevention and Management Strategies
To combat the diabetes epidemic, a comprehensive approach focusing on prevention, early detection, and effective management is crucial. Here are some key strategies:
- Public Health Campaigns: Increasing awareness about diabetes risk factors, promoting healthy lifestyles, and encouraging regular screenings can significantly impact prevention and early detection.
- Healthy Eating: Emphasizing the importance of balanced, nutrient-dense diets can help prevent obesity and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Encouraging the consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean, and healthy fats while limiting processed foods and sugary beverages can contribute to diabetes prevention.
- Regular Physical Activity: Encouraging individuals to exercise regularly is crucial for diabetes prevention and management. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, promotes weight management, and enhances cardiovascular health. Aim for aerobic workouts, strength training, and flexibility exercises. You can discover the benefits of regular physical activity (afternoon and walking) for diabetes control.
- Routine Screening and Early Detection: Regular health check-ups should include screenings for diabetes risk factors, such as blood sugar levels and body mass index (BMI). Early detection allows for timely intervention and management of the condition.
- Medication and Insulin Therapy: For individuals with diabetes, appropriate medication and insulin therapy may be necessary to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. This should be done under the guidance and supervision of healthcare professionals.
- Diabetes Education and Support: Providing access to diabetes education and support programs is crucial for individuals with diabetes. These programs can offer valuable information, guidance on lifestyle modifications, and emotional support to help individuals effectively manage their condition.
- Collaboration Between Healthcare Professionals: Establishing a collaborative approach among healthcare professionals, including primary care physicians, endocrinologists, dietitians, and diabetes educators, ensures comprehensive care for individuals with diabetes. The care plan should include regular follow-ups, medication adjustments, and lifestyle counseling.
The projected rise in global diabetes rates is a cause for concern, necessitating urgent action to curb this epidemic. By understanding the different types of diabetes, addressing the factors contributing to its prevalence, and implementing effective prevention and management strategies, we can strive to mitigate the impact of this chronic condition. Through public health initiatives, education, healthy lifestyle promotion, and accessible healthcare services, we can work towards a healthier future where diabetes rates are reduced and individuals with diabetes can lead fulfilling lives. Let us join forces in combating the diabetes epidemic and prioritizing the health and well-being of our communities.
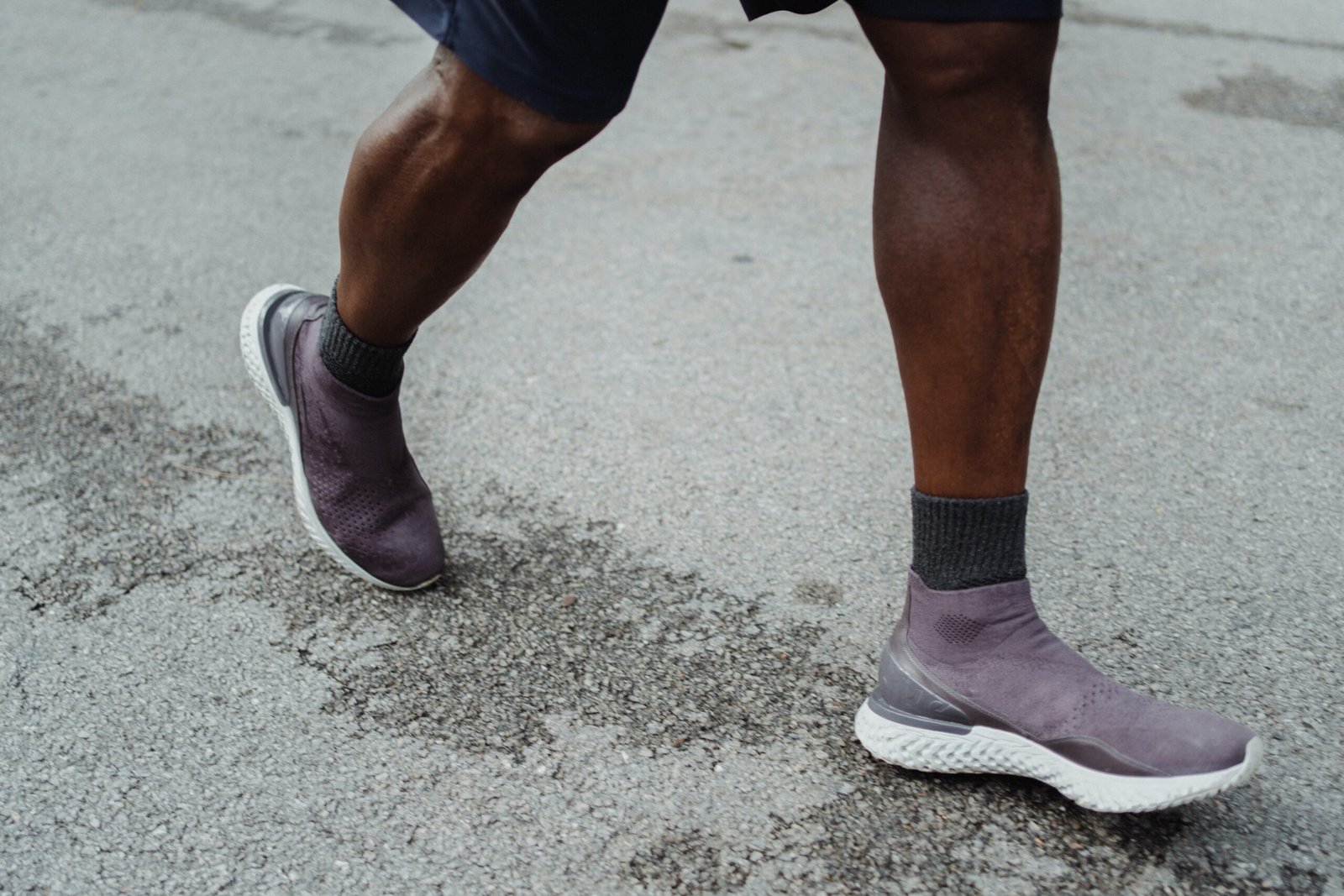

Walking: A Powerful Tool Reducing Your Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
At diabeteslifebalance.com, we are dedicated to providing you with the most valuable and up-to-date information on health and wellness. In this article, we will explore the incredible benefits of walking and how it can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Recent studies have shown compelling evidence that regular walking can play a vital role in maintaining a healthy lifestyle and preventing the onset of this prevalent metabolic disorder. Join us as we delve into the details of this groundbreaking research and uncover the profound impact walking can have on your overall well-being.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from the body’s inability to utilize insulin properly. Diabetes is commonly associated with a sedentary lifestyle, poor dietary choices, obesity, and genetic factors. It affects millions of individuals worldwide and can lead to severe complications if left unmanaged. However, emerging scientific evidence suggests that a simple yet effective solution to mitigate the risk of type 2 diabetes lies in the act of walking.
The Link Between Walking and Reduced Diabetes Risk
A comprehensive study conducted by esteemed researchers has shed light on the profound relationship between walking and preventing type 2 diabetes. The study, which analyzed data from a diverse population over an extended period, found that individuals who engaged in regular walking experienced a significant reduction in their risk of developing this metabolic disorder.
The research showed that walking positively affects our health, including weight management, insulin sensitivity, cardiovascular fitness, and overall metabolic health. By engaging in moderate-intensity walking for at least 30 minutes daily, individuals can witness remarkable improvements in their overall well-being while significantly lowering their risk of type 2 diabetes.
Mechanisms Behind Walking’s Benefits
Walking offers many benefits that contribute to the prevention of type 2 diabetes. Let’s explore some of the fundamental mechanisms through which walking positively impacts our health:
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Walking enhances insulin sensitivity, allowing our cells to utilize glucose effectively. This improved sensitivity leads to better blood sugar control and reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Weight Management: Walking plays a crucial role in managing body weight. It helps burn calories, reduces excess body fat, and promotes a healthy body composition. Maintaining a healthy weight is critical in reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Cardiovascular Health: Regular walking improves cardiovascular fitness by strengthening the heart, enhancing blood circulation, and lowering blood pressure. A healthy cardiovascular system is essential for reducing the risk of developing various chronic diseases, including type 2 diabetes.
- Stress Reduction: Walking offers a natural way to alleviate stress and improve mental well-being. Chronic stress has been linked to increased blood sugar levels and insulin resistance, making stress management a crucial aspect of diabetes prevention.
Incorporating Walking into Your Routine
Now that we understand the profound benefits of walking in reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes let’s explore some practical tips to help you incorporate this healthy habit into your daily routine:
- Start Slowly: If you’re new to walking or physical activity, begin with shorter walks at a comfortable pace. Gradually increase the duration and intensity as your fitness level improves.
- Make It a Habit: Consistency is key. Aim to walk for at least 30 minutes daily, or consider breaking it into smaller sessions throughout the day if it suits your schedule better.
- Find Your Motivation: Walking with a partner, listening to music, or exploring scenic routes can help make your walks more enjoyable and encourage long-term adherence.
- Track Your Progress: Utilize fitness trackers or smartphone apps to monitor your walking progress, such as distance covered, steps taken, and calories burned. Keeping track of your achievements can motivate and help you stay on track toward your goals.
- Make it Social: Consider joining walking groups or participating in community events focused on walking. Engaging with others who share your interest in walking can provide a sense of community and encouragement to maintain your walking routine.
- Incorporate Walking into Daily Activities: Look for opportunities to walk during your daily activities. Park your car farther from your destination, take the stairs instead of the elevator, or go for short walks during your lunch breaks. Every step counts!
In conclusion, walking is a powerful tool in reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Engaging in regular walking not only improves insulin sensitivity, aids in weight management, and enhances cardiovascular health but also contributes to stress reduction and overall well-being. By making walking a part of your daily routine and adopting a proactive approach to your health, you can significantly lower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
At Diabeteslifebalance, we encourage you to prioritize your health and embrace the countless benefits of walking. Remember, every step you take brings you closer to a healthier and more vibrant life. Start walking today and pave the way for a diabetes-free future.
Please note that while walking is an effective method for reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant lifestyle changes or starting a new exercise routine, especially if you have any pre-existing health conditions.
References:
- Hawley, J. A., & Lessard, S. J. (2008). Exercise training-induced improvements in insulin action. Acta Physiologica, 192(1), 127-135.
- Jeon, C. Y., Lokken, R. P., Hu, F. B., & van Dam, R. M. (2007). Physical activity of moderate intensity and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Diabetes care, 30(3), 744-752.
- Knowler, W. C., Barrett-Connor, E., Fowler, S. E., Hamman, R. F., Lachin, J. M., Walker, E. A., & Nathan, D. M. (2002). Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. New England Journal of Medicine, 346(6), 393-403.
DiabetesLifeBalance.com is not affiliated with the mentioned articles or its website. This article is solely created to provide valuable information and promote the benefits of walking in relation to type 2 diabetes risk reduction.
Steps You Need to Take to Prevent Type II Diabetes.
The struggle against type II diabetes has never been more critical. As the rate of this condition continues to climb, it’s time to prioritize our health and wellness, starting with understanding how to reduce our risk of developing this chronic illness. We have created articles and other resources on managing diabetes and achieving balance.
Understanding Type II Diabetes
Type II diabetes is a condition where the body either does not produce enough insulin, or it resists insulin. According to the American Diabetes Association, this can lead to elevated glucose levels in the bloodstream, causing various health issues if left untreated.
Lifestyle Modifications: A Key to Prevention
Studies suggest that lifestyle modifications, such as healthy eating, maintaining a healthy weight, and regular exercise, are effective ways to prevent type II diabetes[^1^].
Eating Healthily to Regulate Blood Sugar
Creating a balanced diet is crucial for reducing the risk of type II diabetes. Opt for whole foods that are low in sugar and saturated fats, such as fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and whole grains[^2^]. Remember, moderation is key, even when it comes to healthy foods. For additional tips on building a diabetes-friendly diet, check out our guide.
Regular Exercise: More Than Just Weight Control
Engaging in regular physical activity not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also improves insulin sensitivity[^3^]. This means that your cells can use available insulin more efficiently, which helps keep your blood sugar levels in check. Even moderate exercise, like brisk walking, can make a significant difference. For exercise inspiration, visit our activity page.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Studies have shown that being overweight increases the risk of type II diabetes[^4^]. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is an excellent way to reduce this risk.
Regular Check-ups: Early Detection, Early Action
Early detection can be a critical factor in preventing the progression of type II diabetes. Regular medical check-ups and blood glucose screenings can help detect prediabetes, which often precedes type II diabetes[^5^].
The Road Ahead
Preventing type II diabetes may seem daunting, but with the right lifestyle modifications, it’s entirely possible. You can significantly reduce your risk by eating healthily, staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, and going for regular check-ups.
It’s time to embark on a healthier, balanced lifestyle journey. For more information and support, visit [https://diabeteslifebalance.com/].
Footnotes
- Mayo Clinic. (2020). Type 2 Diabetes – Symptoms and causes ↩
- Harvard School of Public Health. (2020). Diet Review: Mediterranean Diet ↩
- American Diabetes Association. (2018). Physical Activity/Exercise and Diabetes: A Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association ↩
- [CDC. (2021). Over Weight and Diabetes Risk](https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/risk-factors.html)
- American Diabetes Association. (2018). Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018.https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/41/Supplement_1/S13/30088/2-Classification-and-Diagnosis-of-Diabetes
It’s your journey, your health, and your life. The steps you take today can lead to a healthier, diabetes-free tomorrow. Remember, you’re not alone on this journey. Keep learning, stay motivated, and explore the vast resources available at Diabetes Life Balance.
Start today for a healthier tomorrow!

Type 2 Diabetes: How to Manage & Monitor Your Child’s Blood Sugar
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects people of all ages, including children. It occurs when the body cannot effectively use insulin or does not produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. In recent years, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in children has been on the rise, largely due to lifestyle factors such as poor diet and lack of physical activity.
In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to type 2 diabetes in children, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management. We will also discuss the importance of early detection and provide tips for parents to support their child’s overall health and well-being
1. What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar. As a result, glucose builds up in the bloodstream instead of being used for energy.
While type 2 diabetes is often associated with adults, it is increasingly diagnosed in children and adolescents. This is primarily due to lifestyle factors such as unhealthy eating habits, sedentary behavior, and excess body weight. Genetics and family history also play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes.
2. Causes of Type 2 Diabetes in Children
The exact causes of type 2 diabetes in children are not fully understood. However, several factors contribute to its development:
- Obesity: Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, increases the risk of insulin resistance.
- Unhealthy Diet: Consuming a diet high in sugar, saturated fats, and processed foods can contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary behavior and a lack of exercise reduce the body’s ability to use insulin effectively.
- Family History: Having a close family member with type 2 diabetes increases the risk.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics, and Native Americans, have a higher predisposition to type 2 diabetes.
3. Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes in Children
Recognizing the symptoms of type 2 diabetes in children is crucial for early detection and management. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent Urination: Children may need to urinate more often than usual, including nighttime bedwetting.
- Increased Thirst: Excessive thirst and constant feelings of dehydration.
- Fatigue: Children with type 2 diabetes may experience persistent fatigue and lack of energy.
- Weight Loss or Gain: Unexplained weight loss or weight gain may occur.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels can affect the eyes, causing blurred vision.
- Slow Healing: Wounds or infections may take longer to heal.
- Yeast Infections: Girls may develop frequent yeast infections.
- Darkened Skin: Certain areas of the skin, such as the neck and armpits, may appear darker than usual.
4. Diagnosing Type 2 Diabetes in Children
If you suspect that your child may have type 2 diabetes, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. The diagnosis process typically involves the following:
- Medical History: The doctor will review your child’s medical history and ask about any symptoms or risk factors.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination may be conducted to check for signs of diabetes, such as high blood pressure or darkened skin patches.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests, including fasting blood sugar levels and HbA1c tests, are used to measure blood glucose levels over a period of time.
5. Treatment Options for Children with Type 2 Diabetes
The goal of treatment for children with type 2 diabetes is to manage blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Treatment options may include:
- Lifestyle Changes: Encouraging healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, and weight management.
- Medications: In some cases, oral medications may be prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Insulin Therapy: Insulin injections or an insulin pump may be necessary if lifestyle changes and oral medications alone cannot control blood sugar levels.
6. Lifestyle Changes and Management Strategies
Managing type 2 diabetes in children requires lifestyle changes promoting overall health and well-being. Here are some important strategies:
- Healthy Eating: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit sugary foods and drinks.
- Regular Exercise: Encourage your child to engage in physical activities they enjoy, such as biking, swimming, or dancing. Aim for at least 60 minutes of exercise per day.
- Weight Management: Work with a healthcare professional to develop a weight management plan that is appropriate for your child’s age and growth.
7. Importance of Education and Support
Education and support play a vital role in managing type 2 diabetes in children. Some important aspects to consider include:
- Diabetes Education: Learn about diabetes together with your child. Teach them about blood sugar monitoring, medication management, and the importance of a healthy lifestyle.
- Support Groups: Connect with other families who have children with type 2 diabetes. Sharing experiences and tips can provide valuable support.
- School Involvement: Communicate with your child’s school to ensure they understand the condition and can provide necessary accommodations.
8. Tips for Parents and Caregivers
As a parent or caregiver of a child with type 2 diabetes, providing the necessary support is essential. Here are some tips to help you along the way:
- Be a Role Model: Adopt healthy eating habits and an active lifestyle yourself to set a positive example for your child.
- Create a Supportive Environment: Ensure your home environment promotes healthy choices by stocking nutritious foods and encouraging physical activity.
- Open Communication: Maintain open lines of communication with your child about their diabetes. Encourage them to share any concerns or challenges they may face.
- Routine Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with healthcare professionals to monitor your child’s progress and adjust treatment if needed.
9. Meal Planning and Healthy Eating Habits
Meal planning plays a crucial role in managing type 2 diabetes in children. Here are some helpful tips:
- Balanced Meals: Aim to include a variety of food groups in each meal, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- Portion Control: Teach your child about appropriate portion sizes to avoid overeating.
- Smart Snacking: Encourage healthy snacks such as fruits, vegetables, and nuts instead of sugary snacks or processed foods.
Carbohydrate Management: Monitor and manage the intake of carbohydrates, as they directly affect blood sugar levels. Choose complex carbohydrates and avoid sugary foods and beverages.
- Meal Timing: Establish regular meal times and avoid skipping meals to maintain consistent blood sugar levels.
10. Physical Activity and Exercise Recommendations
Regular physical activity is crucial for children with type 2 diabetes. Consider the following recommendations:
- Age-Appropriate Activities: Engage your child in activities they enjoy, such as biking, swimming, or team sports.
- Screen Time Limitations: Limit sedentary activities, such as excessive screen time, and encourage active play instead.
- Structured Exercise: Aim for at least 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity each day. This can be broken down into smaller sessions throughout the day.
11. Emotional Well-being and Mental Health
Living with type 2 diabetes can have emotional and mental health implications for children. Here’s how you can support their well-being:
- Open Communication: Create a safe space for your child to express their feelings and concerns about their condition.
- Positive Reinforcement: Recognize and celebrate your child’s efforts in managing their diabetes and making healthy choices.
- Stress Management: Teach your child stress management techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or engaging in relaxing activities.
12. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial to manage type 2 diabetes in children effectively. Consider the following:
- Blood Glucose Testing: Work with your healthcare team to determine how frequently your child should test their blood sugar levels.
- Target Ranges: Understand the target blood sugar range for your child and take appropriate actions based on the results.
- Record Keeping: Maintain a log of blood sugar readings to identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
13. Medications and Insulin Therapy
In some cases, children with type 2 diabetes may require medications or insulin therapy to manage their condition. Here’s what you need to know:
- Oral Medications: Some children may be prescribed oral medications, such as metformin, to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Insulin Therapy: If oral medications are not sufficient, your child may need insulin therapy. This can be administered through injections or an insulin pump.
- Careful Monitoring: Regularly monitor your child’s response to medications or insulin therapy and consult with healthcare professionals for any necessary adjustments.
14. Potential Complications of Type 2 Diabetes in Children
While managing type 2 diabetes is crucial, it’s also important to be aware of potential complications. These can include:
- Heart Disease: Children with type 2 diabetes are at a higher risk of developing heart disease later in life.
- Kidney Disease: Poorly controlled blood sugar levels can lead to kidney damage over time.
- Eye Problems: Diabetes can affect the eyes and increase the risk of conditions such as retinopathy or cataracts.
- Nerve Damage: Long-term high blood sugar levels can cause nerve damage, leading to issues such as numbness or tingling in the hands and feet.
Managing type 2 diabetes in children requires a comprehensive approach that focuses on lifestyle changes, education, support, and medical intervention when necessary. By promoting healthy habits, monitoring blood sugar levels, and providing emotional support, parents and caregivers can help their child live a fulfilling life while effectively managing their condition.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Can type 2 diabetes in children be prevented?
Type 2 diabetes can sometimes be prevented or delayed by implementing healthy lifestyle habits from an early age. This includes promoting a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Is type 2 diabetes reversible in children?
While type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition, lifestyle changes and proper management can help control blood sugar levels effectively. With early intervention and consistent adherence to a healthy lifestyle, some children may be able to achieve normal blood sugar levels and reduce the need for medication or insulin therapy. - Can my child with type 2 diabetes still enjoy treats and desserts?
Yes, your child can still enjoy treats and desserts in moderation. Teaching them about portion control and making healthier choices, such as opting for low-sugar or sugar-free alternatives, is essential. Incorporating treats into a balanced meal plan can help them manage their blood sugar levels effectively. - Should my child with type 2 diabetes participate in physical activities and sports?
Absolutely! Physical activity is highly beneficial for children with type 2 diabetes. Regular exercise and sports can help improve insulin sensitivity, promote weight management, and enhance overall well-being. However, it is essential to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure appropriate precautions are taken to prevent any complications. - How can I support my child emotionally in dealing with type 2 diabetes?
Supporting your child emotionally is crucial in their diabetes management. Listen to their concerns, provide reassurance, and encourage open communication. Help them build a support network by connecting with other families facing similar challenges. Consider involving them in decision-making regarding their diabetes management to empower them and foster a sense of control.
Understanding the Impact of Stigma and Fear on Healthcare Appointments for People Living with Diabetes
Living with diabetes can present various challenges, from managing blood sugar levels to making lifestyle adjustments. However, a recent report from Diabetes UK has shed light on a concerning issue – approximately 50% of people with diabetes have missed healthcare appointments due to stigma and fear. This article will delve into the reasons behind this phenomenon, its implications for diabetes management, and potential strategies to address the issue.
The Stigma Surrounding Diabetes
What is Stigma?
Stigma refers to the negative attitudes and beliefs that society holds towards certain conditions or groups of people. Unfortunately, diabetes is not exempt from this social stigma. Individuals living with diabetes may face judgment, stereotypes, and discrimination due to misconceptions about the condition.
The Impact of Stigma
Stigma can have a profound impact on the lives of people with diabetes. It can lead to feelings of shame, embarrassment, and self-blame, making it challenging for individuals to seek appropriate healthcare. Fear of being labeled, judged, or misunderstood may prevent them from attending crucial medical appointments, which is essential for managing their condition effectively.
Fear and Healthcare Avoidance
Fear of Judgment and Misunderstanding
Many individuals with diabetes experience fear when it comes to healthcare appointments. They worry about being judged or misunderstood by healthcare professionals due to misconceptions about the condition. This fear can be particularly pronounced when individuals have faced previous negative experiences or encounters with healthcare providers.
Emotional and Psychological Factors
The fear of healthcare appointments can be rooted in emotional and psychological factors. Some individuals may feel overwhelmed by the burden of managing their condition and fear hearing bad news or being reminded of their health challenges. These anxieties can contribute to avoidance behavior and a reluctance to engage with healthcare services.
Practical Barriers
In addition to emotional factors, practical barriers can contribute to missed healthcare appointments. Factors such as transportation issues, financial constraints, or scheduling conflicts may make it difficult for individuals to attend their appointments, leading to further avoidance.
Implications for Diabetes Management
Poor Glycemic Control
Missed healthcare appointments can have significant consequences for diabetes management. Regular check-ups and monitoring are crucial for maintaining optimal glycemic control. When individuals avoid these appointments, they may struggle to adjust their treatment plans, leading to suboptimal blood sugar management and an increased risk of complications.
Delayed Intervention and Treatment
Timely intervention is essential for preventing complications and managing diabetes effectively. When individuals miss healthcare appointments, potential health concerns or complications may go undetected, leading to necessary treatment and interventions delays.
Psychological and Emotional Well-being
Stigma and fear can also take a toll on the psychological and emotional well-being of individuals with diabetes. Avoiding healthcare appointments can exacerbate anxiety and stress, potentially leading to increased feelings of isolation and depression. By addressing the underlying factors contributing to missed appointments, we can support the overall well-being of individuals living with diabetes.
Addressing Stigma and Fear: Strategies for Change
Raising Awareness and Education
One of the key strategies for combating stigma and fear surrounding diabetes is through education and awareness campaigns. By dispelling myths and providing accurate information about the condition, we can reduce the misconceptions contributing to stigma. Additionally, educating healthcare professionals about the impact of stigma and how to create a supportive environment can enhance the overall patient experience.
Creating Supportive Environments
Healthcare settings play a crucial role in fostering a supportive and inclusive environment for individuals with diabetes. Implementing patient-centered care approaches, where individuals feel respected, heard, and understood, can help alleviate fears and reduce stigma. This can be achieved through healthcare provider training programs that emphasize empathy, cultural sensitivity, and practical communication skills.
Peer Support and Community Engagement
Connecting individuals with diabetes to peer support groups and community resources can be instrumental in addressing feelings of isolation and building a sense of belonging. Peer support offers a safe space for individuals to share experiences, seek guidance, and receive emotional support from those who can relate to their challenges. Community engagement initiatives, such as diabetes awareness events and workshops, can also foster a sense of empowerment and reduce the stigma associated with the condition.
Addressing Practical Barriers
To ensure individuals with diabetes can access healthcare services without unnecessary obstacles, it is essential to address practical barriers. This can involve providing transportation assistance, flexible appointment scheduling options, and exploring financial support programs for those facing financial constraints. Addressing these practical challenges makes individuals more likely to attend their healthcare appointments and receive the necessary care.
The impact of stigma and fear on healthcare appointments for people living with diabetes is a significant concern that requires attention and action. By understanding the factors contributing to missed appointments, healthcare providers, policymakers, and communities can work together to create supportive environments that promote engagement, reduce stigma, and improve diabetes management. Through education, awareness, and targeted interventions, we can empower individuals to overcome their fears, access the healthcare they need, and enhance their overall well-being.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- How does stigma affect individuals living with diabetes?
Stigma can lead to feelings of shame, embarrassment, and self-blame, making it challenging for individuals to seek appropriate healthcare and manage their condition effectively. - What are the consequences of missed healthcare appointments for people with diabetes?
Missed appointments can result in poor glycemic control, delayed intervention and treatment, and negatively impact the psychological and emotional well-being of individuals with diabetes. - What strategies can help address the stigma and fear surrounding diabetes?
Raising awareness and education, creating supportive environments, promoting peer support and community engagement, and addressing practical barriers are effective strategies to combat stigma and fear. - How can healthcare providers contribute to reducing stigma and fear?
Healthcare providers can undergo training programs that emphasize empathy, cultural sensitivity, and effective communication skills to create a supportive environment for individuals with diabetes. - What role does community engagement play in addressing stigma and fear?
Community engagement initiatives, such as diabetes awareness events and peer support groups, foster a sense of empowerment, reduce isolation, and help individuals with diabetes overcome stigma and fear.

Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Type 2 Diabetes for Men Under 40
So, have you ever wondered about your health’s ticking clock? As men under 40, we often perceive ourselves as invincible, ignoring silent but potential risks. One such overlooked condition is Type 2 diabetes. It’s more than high blood sugar; it’s a lifelong fight, and it’s about time we got familiar with it.
The Unseen Enemy – Type 2 Diabetes
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes occurs when our bodies resist insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating sugar. It’s like a key that no longer fits the lock, causing sugar to build up in our blood.
Why Should Men Under 40 Care?
Despite common belief, Type 2 diabetes isn’t an “old man’s disease.” Recent studies show a rise in young adults diagnosed; shockingly, men under 40 are at higher risk.
The Warning Signs – Detect Early, Act Promptly
Symptoms to Look Out For
From increased thirst to unexplained weight loss, these signs can seem trivial but might be the body’s SOS for help.
Risk Factors
Ever wondered if you’re at risk? Family history, weight, and lifestyle can make the difference between a diabetes-free life and a lifetime of medications.
The Lifesaver – Prevention Is Better Than Cure
Embrace a Healthy Lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle can often prevent Type 2 diabetes. It’s not about drastic changes; it’s about smart choices. Remember, Rome wasn’t built in a day!
Regular Check-ups and Screenings
If prevention is the first step, detection is the second. Regular check-ups can help identify the risk early and nip it in the bud. Remember to talk to your doctor, and most importantly GO to the doctor.
The Battlefront – Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Diet And Exercise
Healthy eating and physical activity are crucial. It’s not about denying ourselves pleasures but finding a balance. Look online for healthy and delicious meal plans. And physical activity can be as simple as taking a walk for your break instead of staying seated at your desk.
Medications And Insulin Therapy
Sometimes, lifestyle changes aren’t enough. Medications and insulin therapy can help our bodies overcome resistance and use insulin effectively.
The Road Ahead – Living With Type 2 Diabetes
Mental Health And Emotional Well-being
Living with diabetes isn’t just about managing blood sugar levels. It also means dealing with emotional stress and mental health challenges that come along the way.
Diabetes Doesn’t Define You
Remember, we are much more than a diagnosis. We can live fulfilling lives with diabetes, defining our path and writing our own story.
Conclusion
We’ve walked through the battlefield of Type 2 diabetes, understanding its risks, prevention, and management. Remember, it’s a journey, not a destination. Together, we can beat the odds and prove that Type 2 diabetes is conquerable, not inevitable.
Pfizer’s Diabetes Drug: Weight Reduction Similar to Novo Nordisk’s Ozempic
In contemporary medical advancements, the esteemed pharmaceutical titan, Pfizer, has unveiled noteworthy triumphs in diabetes management. Their recent investigational endeavors have yielded heartening results for their diabetes therapeutic, showcasing an impressive capacity for weight diminution akin to Novo Nordisk’s Ozempic. This development has sparked a wave of optimism amongst health professionals. Mainly due to the immense health issues that obesity and diabetes pose on a global scale.
Dissecting the Influence of Diabetes and Obesity
Diabetes, an enduring health anomaly, is delineated by heightened glucose concentrations in the bloodstream, a consequence of the body’s impaired production or suboptimal utilization of insulin. This malady afflicts countless individuals across the globe, potentially culminating in grave complications like cardiac disease, nephrological impairment, and vision loss.
Contrastingly, obesity, a colossal risk contributor to type 2 diabetes, is defined by surplus body mass and excessive adipose tissue accrual. The omnipresence of obesity has manifested a consistent upward trajectory, thereby catalyzing an augmentation in the global prevalence of diabetes.
The Quintessence of Therapeutics in Diabetes Amelioration
The cornerstone of diabetes management rests on an amalgamation of lifestyle metamorphoses—dietary transformations and physical exertion—with therapeutic intervention. Medications are indispensable in modulating glucose concentrations, amplifying insulin receptivity, and mitigating complication probabilities.
Pfizer’s Anti-Diabetic Pharmaceutical: A Potential Paradigm Shift
The anti-diabetic pharmaceutical in Pfizer’s pipeline, presently in the clinical assessment phase, has manifested an encouraging efficacy in weight diminution. This therapeutic belongs to the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) family, paralleling Novo Nordisk’s Ozempic. GLP-1 RAs emulate the functionality of a hormone dubbed glucagon-like peptide-1, which incites insulin excretion and appetite suppression.
The recent probe by Pfizer encompassed a sizable group of overweight or obese individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. The analysis elucidated a notable contraction in body mass among recipients of Pfizer’s pharmaceutical, mirroring the weight abatement witnessed in individuals administered with Ozempic. This inference implies that Pfizer’s anti-diabetic pharmaceutical might emerge as a pragmatic alternative for those grappling with the dual challenge of diabetes and obesity.
Merits of Pfizer’s Anti-Diabetic Pharmaceutical
Weight Diminution: Pfizer’s anti-diabetic pharmaceutical’s extraordinary proficiency in weight diminution is of immense significance. Obesity management is pivotal in diabetes care as it augments insulin sensitivity and curtails complication risks. Enhanced Glycemic Regulation: GLP-1 RAs, inclusive of Pfizer’s therapeutic, have validated their effectiveness in bolstering glycemic regulation by diminishing glucose concentrations. This influence can facilitate individuals in achieving superior diabetes regulation and curtail the exigency for supplementary therapeutics. Cardiovascular Prospects: Certain GLP-1 RAs have demonstrated cardiovascular prospects by attenuating the risk of cardiac events, strokes, and deaths resulting from cardiovascular anomalies. Additional exploration is imperative to ascertain if Pfizer’s pharmaceutical exhibits these favorable influences. Clinical Consequences and Future Investigations The prospective advantages of Pfizer’s anti-diabetic pharmaceutical are substantial, yet auxiliary research is required to ascertain its safety profile, efficiency, and enduring impacts. Clinical explorations involving more extensive and more heterogeneous patient clusters are crucial to corroborate the preliminary discoveries and inspect any prospective adverse effects or interactions with concomitant medications.
If ensuing investigations substantiate the success of Pfizer’s therapeutic and secure regulatory endorsement, it could furnish a novel treatment avenue for individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes who are concurrently combating obesity. This would constitute a valuable expansion to the existing repertoire of anti-diabetic therapeutics, enabling physicians and patients to have an enhanced arsenal for tailor-made care.
Pfizer’s anti-diabetic pharmaceutical has showcased heartening results in weight reduction, echoing the efficacy of Novo Nordisk’s Ozempic. This innovative stride offers hope to individuals suffering from type 2 diabetes who are concurrently battling obesity. The unique ability of Pfizer’s drug to tackle both conditions concurrently could potentially herald a new chapter in diabetes management and obesity reduction. This could signal a seismic shift in our approach toward these widespread health challenges, equipping us with another potent tool in our ongoing battle against these common yet complex conditions.
Revolutionary Effects of Ozempic on Diabetes and Weight Loss
Recent groundbreaking research indicates that Ozempic, a drug commonly used for managing type 2 diabetes, has displayed significant potential in promoting weight loss. It is revolutionizing our understanding of treatment strategies for diabetes and obesity, two of the most prevalent health issues in the modern world. Ozempic:
An Overview
Ozempic, scientifically known as semaglutide, is an injectable medication traditionally prescribed to adults suffering from type 2 diabetes. It aids in controlling blood sugar levels by mimicking the action of a hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which increases insulin production while reducing glucose production in the liver.
The Interplay between Diabetes and Obesity
Diabetes and obesity often go hand in hand. Excess weight can lead to insulin resistance, causing the body’s cells to use insulin less efficiently. This imbalance results in higher glucose levels in the blood, setting the stage for type 2 diabetes. Thus, managing weight effectively is a critical component of diabetes control.
Ozempic’s Role in Weight Loss
A series of groundbreaking studies have shed light on the weight-loss benefits of Ozempic. They revealed that this GLP-1 receptor agonist could help patients lose weight by making them feel full more quickly, thereby reducing overall food intake. This unexpected benefit was discovered during diabetes management treatment and has brought forth a new perspective on tackling obesity. Clinical Studies and Findings Several clinical trials have indicated the promising weight loss potential of Ozempic. One of the landmark studies was the SUSTAIN trial series. In these trials, patients with type 2 diabetes and those with obesity but without diabetes were administered with semaglutide. The results showed an impressive weight loss, especially in the obesity group, emphasizing the effectiveness of Ozempic in managing weight.
Unleashing a New Potential
The findings have led to a newfound interest in the therapeutic potential of Ozempic beyond its traditional use in managing diabetes. Researchers are now investigating the effectiveness of Ozempic in the treatment of obesity, heralding a new era of medical breakthroughs. Ozempic: A Dual-Purpose Solution The potential dual-purpose role of Ozempic – diabetes management and weight loss – offers hope for millions of people worldwide. It signifies a massive leap in healthcare, providing an effective solution for two of the most significant health challenges of our time.
The Future of Ozempic in Weight Loss
Ongoing research continues to explore the comprehensive benefits of Ozempic in diabetes and obesity treatment. It presents an exciting prospect for the future, especially considering the increasing prevalence of these health conditions worldwide. The full scope of Ozempic’s potential is still being uncovered, and the journey towards revolutionizing healthcare has only just begun.
In conclusion, Ozempic is a ground-breaking drug transforming the landscape of diabetes and obesity management. It offers a beacon of hope for patients worldwide, paving the way for novel treatment strategies that could significantly enhance the quality of life for millions of people. The journey to fully uncovering the potential of Ozempic is still underway, and it promises to reshape our understanding of disease management in the coming years.


